The immunopathogenesis of fibrosis in systemic sclerosis
- PMID: 30430560
- PMCID: PMC6378383
- DOI: 10.1111/cei.13238
The immunopathogenesis of fibrosis in systemic sclerosis
Abstract
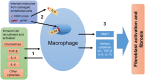
Systemic sclerosis (SSc) is an idiopathic systemic autoimmune disease. It is characterized by a triad of hallmarks: immune dysfunction, fibrosis and vasculopathy. Immune dysfunction in SSc is characterized by the activation and recruitment of immune cells and the production of autoantibodies and cytokines. How immune abnormalities link the fibrosis and vasculopathy in SSc is poorly understood. A plethora of immune cell types are implicated in the immunopathogenesis of SSc, including T cells, B cells, dendritic cells, mast cells and macrophages. How these different cell types interact to contribute to SSc is complicated, and can involve cell-to-cell interactions and communication via cytokines, including transforming growth factor (TGF)-β, interleukin (IL)-6 and IL-4. We will attempt to review significant and recent research demonstrating the importance of immune cell regulation in the immunopathogenesis of SSc with a particular focus on fibrosis.
Keywords: B cells; T cells; Toll-like receptors (TLRs); arthritis (including rheumatoid arthritis).
© 2018 British Society for Immunology.
Figures
References
-
- Asano Y, Sato S. Vasculopathy in scleroderma. Semin Immunopathol 2015; 37:489–500. - PubMed
-
- McGaha T et al Lack of skin fibrosis in tight skin (TSK) mice with targeted mutation in the interleukin‐4R alpha and transforming growth factor‐beta genes. J Invest Dermatol 2001; 116:136–43. - PubMed
-
- Fertin C et al Interleukin‐4 stimulates collagen synthesis by normal and scleroderma fibroblasts in dermal equivalents. Cell Mol Biol 1991; 37:823–9. - PubMed
-
- Sempowski GD, Derdak S, Phipps RP. Interleukin‐4 and interferon‐gamma discordantly regulate collagen biosynthesis by functionally distinct lung fibroblast subsets. J Cell Physiol 1996; 167:290–6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

