High-pressure carbon dioxide pneumoperitoneum induces oxidative stress and mitochondria-associated apoptotic pathway in rabbit kidneys with severe hydronephrosis
- PMID: 30431064
- PMCID: PMC6257853
- DOI: 10.3892/ijmm.2018.3986
High-pressure carbon dioxide pneumoperitoneum induces oxidative stress and mitochondria-associated apoptotic pathway in rabbit kidneys with severe hydronephrosis
Abstract
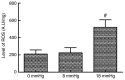
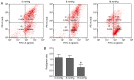
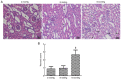
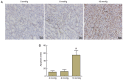
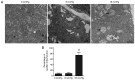
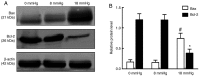
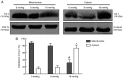
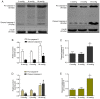
The primary aim of the present study was to investigate the potential effect of high‑pressure carbon dioxide (CO2) pneumoperitoneum on kidneys with severe hydronephrosis and to investigate the possible underlying mechanism. A total of 18 rabbits underwent a surgical procedure inducing severe hydronephrosis. Rabbits were then divided at random into three groups (n=6 each) and subjected to intraabdominal pressure of 0, 8 or 18 mmHg, respectively. CO2 inflation lasted for 90 min in the pneumoperitoneum groups. Oxidative stress was assessed by measurements of reactive oxygen species (ROS). Activation of apoptosis was analyzed by western blot analysis of B‑cell lymphoma 2 (Bcl‑2), Bcl‑2‑associated x protein (Bax), cytochrome c (Cyt c), caspase‑3 and caspase‑9 levels. In addition, TUNEL assay, hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining, measurement of mitochondrial membrane potential (MMP) and detection of changes to kidney ultramicrostructure were performed. In the 0 and 8 mmHg groups, all results were normal and similar. However, in the 18 mmHg group, the kidneys suffered oxidative damage and mitochondrial injuries, and increased ROS levels, lower MMP and mitochondrial vacuolization were observed. Furthermore, the mitochondrial/caspase‑dependent pathway of apoptosis was activated, as indicated by the apoptotic index, and the expression levels and translocation of Bax, Bcl‑2, Cyt c, caspase‑3 and caspase‑9. Therefore, it is concluded that high‑pressure CO2 pneumoperitoneum induces oxidative damage and apoptosis in rabbit kidneys with severe hydronephrosis, which is associated with the mitochondrial apoptotic pathway.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Oxidative damage and mitochondrial injuries differ following pneumoperitoneum pressure in rabbit models of varying degrees of hydronephrosis.Mol Med Rep. 2018 May;17(5):6819-6827. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2018.8665. Epub 2018 Mar 1. Mol Med Rep. 2018. PMID: 29512718
-
Oxidative Damage and Mitochondrial Injuries Are Induced by Various Irrigation Pressures in Rabbit Models of Mild and Severe Hydronephrosis.PLoS One. 2015 Jun 19;10(6):e0127143. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0127143. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26090815 Free PMC article.
-
Acute Kidney Injury Induced by Pneumoperitoneum Pressure Via a Mitochondrial Injury-dependent Mechanism in a Rabbit Model of Different Degrees of Hydronephrosis.Urology. 2019 May;127:134.e1-134.e7. doi: 10.1016/j.urology.2019.02.006. Epub 2019 Feb 19. Urology. 2019. PMID: 30790647
-
Two clinically relevant pressures of carbon dioxide pneumoperitoneum cause hepatic injury in a rabbit model.World J Gastroenterol. 2011 Aug 21;17(31):3652-8. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v17.i31.3652. World J Gastroenterol. 2011. PMID: 21987614 Free PMC article.
-
Methyl antcinate A from Antrodia camphorata induces apoptosis in human liver cancer cells through oxidant-mediated cofilin- and Bax-triggered mitochondrial pathway.Chem Res Toxicol. 2010 Jul 19;23(7):1256-67. doi: 10.1021/tx100116a. Chem Res Toxicol. 2010. PMID: 20557081
Cited by
-
A comprehensive transcriptional reference for severity and progression in spinal cord injury reveals novel translational biomarker genes.J Transl Med. 2025 Feb 4;23(1):160. doi: 10.1186/s12967-024-06009-6. J Transl Med. 2025. PMID: 39905473 Free PMC article.
-
Hydromorphone Protects against CO2 Pneumoperitoneum-Induced Lung Injury via Heme Oxygenase-1-Regulated Mitochondrial Dynamics.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021 Apr 9;2021:9034376. doi: 10.1155/2021/9034376. eCollection 2021. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021. PMID: 33927798 Free PMC article.
-
Carbon Dioxide Pneumoperitoneum May Alter Ovarian Apoptosis: An Experimental Study.Gynecol Minim Invasive Ther. 2021 Apr 14;10(2):91-95. doi: 10.4103/GMIT.GMIT_96_20. eCollection 2021 Apr-Jun. Gynecol Minim Invasive Ther. 2021. PMID: 34040967 Free PMC article.
-
The Effects of Lactobacillus plantarum-12 Crude Exopolysaccharides on the Cell Proliferation and Apoptosis of Human Colon Cancer (HT-29) Cells.Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins. 2021 Apr;13(2):413-421. doi: 10.1007/s12602-020-09699-8. Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins. 2021. PMID: 32844363
-
Exploration the potential mechanism of the SIRT1 and its target gene FOXO1/PPARGC1A in uteropelvic junction obstruction.Transl Androl Urol. 2021 Nov;10(11):4192-4205. doi: 10.21037/tau-21-752. Transl Androl Urol. 2021. PMID: 34984185 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Seims AD, VanHouwelingen L, Mead J, Mao S, Loh A, Sandoval JA, Davidoff AM, Wu J, Wang WC. Operative and immediate postoperative differences between traditional multiport and reduced port laparoscopic total splenectomy in pediatric patients. J Laparoendosc Adv Surg Tech A. 2017;27:206–210. doi: 10.1089/lap.2016.0309. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

