20(S)-ginsenoside-Rg3 reverses temozolomide resistance and restrains epithelial-mesenchymal transition progression in glioblastoma
- PMID: 30431207
- PMCID: PMC6317960
- DOI: 10.1111/cas.13881
20(S)-ginsenoside-Rg3 reverses temozolomide resistance and restrains epithelial-mesenchymal transition progression in glioblastoma
Abstract
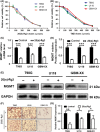
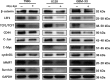
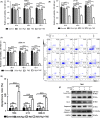
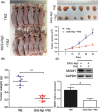
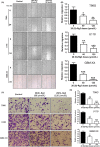
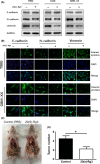
Glioblastoma multiforme (GBM) is one of the most malignant human intracranial tumors. Temozolomide (TMZ) is the primary alkylating agent for GBM patients. However, many GBM patients are resistant to TMZ. Therefore, patients with GBM urgently need more effective therapeutic options. 20(S)-ginsenoside-Rg3 (20(S)-Rg3) is a natural chemical with anti-tumor effects, but at present there is little understanding of its functional mechanism. Several research reports have demonstrated that O6 -methylguanine DNA-methyltransferase (MGMT) repairs damaged DNA and contributes to TMZ resistance in gliomas. In addition, recent studies have shown that MGMT gene expression could be regulated by the Wnt/β-catenin pathway. However, whether 20(S)-Rg3 inhibits MGMT expression and augments chemosensitivity to Temozolomide (TMZ) in glioma cells remains unclear. In this study, we explored the modulating effects of 20(S)-Rg3 on MGMT. We used glioma cell lines, primary cell strain (including T98G, U118 and GBM-XX; all of them are MGMT-positive glioma cell lines) and xenograft glioma models to examine whether 20(S)-Rg3 increased the sensitivity to TMZ and to reveal the underlying mechanisms. We found that the MGMT expression was effectively downregulated by 20(S)-Rg3 via the Wnt/β-catenin pathway in glioma cell lines, and TMZ resistance was significantly reversed by 20(S)-Rg3. Meanwhile, 20(S)-Rg3 shows no obvious cytotoxicity at its effective dose and is well tolerated in vivo. In addition, we found that 20(S)-Rg3 significantly restrains the epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) progression of glioma cells. Taken together, these results indicate that 20(S)-Rg3 may be a novel agent to use in treatment of GBM, especially in TMZ-resistant GBM with high MGMT expression.
Keywords: 20(S)-ginsenoside-Rg3; O6-methylguanine DNA-methyltransferase; Wnt/β-catenin pathway; glioblastoma multiforme; temozolomide.
© 2018 The Authors. Cancer Science published by John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd on behalf of Japanese Cancer Association.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Pharmacological inhibition of serine synthesis enhances temozolomide efficacy by decreasing O6-methylguanine DNA methyltransferase (MGMT) expression and reactive oxygen species (ROS)-mediated DNA damage in glioblastoma.Lab Invest. 2022 Feb;102(2):194-203. doi: 10.1038/s41374-021-00666-7. Epub 2021 Oct 8. Lab Invest. 2022. PMID: 34625658
-
β-catenin contributes to cordycepin-induced MGMT inhibition and reduction of temozolomide resistance in glioma cells by increasing intracellular reactive oxygen species.Cancer Lett. 2018 Oct 28;435:66-79. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2018.07.040. Epub 2018 Aug 4. Cancer Lett. 2018. PMID: 30081068
-
Natural small molecule thymoquinone increases the chemosensitivity of glioblastoma to temozolomide through inhibiting Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway to downregulate MGMT expression: In vitro and in vivo validation.Biochem Pharmacol. 2025 Jun;236:116886. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2025.116886. Epub 2025 Mar 22. Biochem Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40127739
-
Unlocking temozolomide resistance in glioblastoma: the pivotal role of MicroRNAs and in-silico insights.Med Oncol. 2025 Jul 17;42(8):343. doi: 10.1007/s12032-025-02884-1. Med Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40676394 Review.
-
Anti-glioma therapy with temozolomide and status of the DNA-repair gene MGMT.Anticancer Res. 2009 Nov;29(11):4845-54. Anticancer Res. 2009. PMID: 20032445 Review.
Cited by
-
Pharmacological inhibition of serine synthesis enhances temozolomide efficacy by decreasing O6-methylguanine DNA methyltransferase (MGMT) expression and reactive oxygen species (ROS)-mediated DNA damage in glioblastoma.Lab Invest. 2022 Feb;102(2):194-203. doi: 10.1038/s41374-021-00666-7. Epub 2021 Oct 8. Lab Invest. 2022. PMID: 34625658
-
Targeting Pivotal Hallmarks of Cancer for Enhanced Therapeutic Strategies in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Treatment-In Vitro, In Vivo and Clinical Trials Literature Review.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Apr 12;16(8):1483. doi: 10.3390/cancers16081483. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38672570 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of Non-coding RNAs in the Response of Glioblastoma to Temozolomide.Mol Neurobiol. 2025 Feb;62(2):1726-1755. doi: 10.1007/s12035-024-04316-z. Epub 2024 Jul 18. Mol Neurobiol. 2025. PMID: 39023794 Review.
-
Enhanced Inhibition of Tumorigenesis Using Combinations of miRNA-Targeted Therapeutics.Front Pharmacol. 2019 May 16;10:488. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2019.00488. eCollection 2019. Front Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 31156429 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ginsenoside Rg3: A Review of its Anticancer Mechanisms and Potential Therapeutic Applications.Curr Top Med Chem. 2024;24(10):869-884. doi: 10.2174/0115680266283661240226052054. Curr Top Med Chem. 2024. PMID: 38441023 Review.
References
-
- Lapointe S, Perry A, Butowski NA. Primary brain tumours in adults. Lancet (London, England). 2018;392(10145):432‐446. - PubMed
-
- Stupp R, Mason WP, van den Bent MJ, et al. Radiotherapy plus concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide for glioblastoma. N Engl J Med. 2005;352(10):987‐996. - PubMed
-
- Stupp R, Brada M, van den Bent MJ, Tonn JC, Pentheroudakis G. High‐grade glioma: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow‐up. Ann Oncol. 2014;25(Suppl 3):iii93‐iii101. - PubMed
-
- Stupp R, Hegi ME, Mason WP, et al. Effects of radiotherapy with concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide versus radiotherapy alone on survival in glioblastoma in a randomised phase III study: 5‐year analysis of the EORTC‐NCIC trial. Lancet Oncol. 2009;10(5):459‐466. - PubMed
-
- Wen PY, Kesari S. Malignant gliomas in adults. N Engl J Med. 2008;359(5):492‐507. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

