Zusanli (ST36) Acupoint Injection for Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy: A Systematic Review of Randomized Controlled Trials
- PMID: 30431314
- PMCID: PMC6987730
- DOI: 10.1089/acm.2018.0053
Zusanli (ST36) Acupoint Injection for Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy: A Systematic Review of Randomized Controlled Trials
Abstract
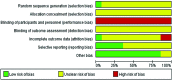
Background: Acupuncture point (acupoint) injection is a common practice in China. Some trials showed that Chinese herbal extracts and/or conventional medication are injected at the Zusanli (ST36) acupoint for the treatment of diabetic peripheral neuropathy (DPN). The study aimed to assess the effectiveness and safety of acupoint injection for DPN at the ST36 by systematically evaluating the evidence published to date. Methods: Six databases were searched for randomized controlled trials (RCTs) of ST36 injection for DPN with primary outcome of pain, global symptom improvement, and quality of life. Methodological quality was assessed by the Cochrane risk of bias (ROB) tool. Data were analyzed using RevMan 5.3. Results: Fourteen RCTs involving 1,071 participants with DPN were included. All RCTs were assessed as unclear or high ROB. Few RCTs adequately reported methodology-related items and needling details according to Consolidated Standards of Reporting Trials (CONSORT) and Standards for Reporting Interventions in Controlled Trials of Acupuncture (STRICTA) statement. Medications injected at ST36 included conventional medications (11 RCTs) and Chinese herbal extracts (3 RCTs). The authors of this study did not perform any meta-analysis due to the heterogeneity of medications used for injections. Two individual RCTs favored ST36 injection in relieving pain compared with intramuscular injection of the same medication. For global symptom measured by Toronto clinical scoring system, one RCT showed that ST36 injection of Fufang Danggui was more effective than intramuscular injection of vitamin B12, two RCTs demonstrated that ST36 injection of mecobalamin or Danhong with cointervention was superior, while one RCT showed no significant differences between ST36 injection and intramuscular injection of mecobalamin. For improving nerve conduction velocity (NCV), three of four individual RCTs showed that ST36 injection was better than intramuscular or intravenous injection of the same medication, two RCTs favored ST36 injection with cointervention, and one RCT favored ST36 injection without cointervention. Four RCTs reported monitoring adverse events, all of which showed no significant difference between groups. Conclusions: Limited evidence suggests that ST36 injection appears to be safe, and potentially effective in reducing pain score and improving NCV compared with intramuscular injection of the same medication. However, poor methodological and reporting quality reduced confidence in the findings. Rigorously designed and well-reported RCTs evaluating the effectiveness of ST36 injection for DPN are warranted.
Keywords: ST36; Zusanli; acupoint injection; diabetic peripheral neuropathy; randomized controlled trials; systematic review.
Conflict of interest statement
No competing financial interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Diffusion Tensor Imaging Evaluates Effects of Acupoint Injection at Zusanli (ST36) for Type 2 Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy.Med Sci Monit. 2022 Jun 29;28:e935979. doi: 10.12659/MSM.935979. Med Sci Monit. 2022. PMID: 35765223 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Traditional Chinese medicine foot bath combined with acupoint massage for the treatment of diabetic peripheral neuropathy: A systematic review and meta-analysis of 31 RCTs.Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2020 Feb;36(2):e3218. doi: 10.1002/dmrr.3218. Epub 2019 Oct 29. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2020. PMID: 31659861
-
Acupuncture for the treatment of lower limb diabetic peripheral neuropathy: a systematic review.Acupunct Med. 2019 Feb;37(1):3-15. doi: 10.1136/acupmed-2018-011666. Epub 2019 Mar 22. Acupunct Med. 2019. PMID: 30900484
-
Zusanli (ST36) acupoint injection for acute diarrhea in children under 5 years old: A protocol of systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials.Medicine (Baltimore). 2019 Aug;98(34):e16949. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000016949. Medicine (Baltimore). 2019. PMID: 31441891 Free PMC article.
-
Chinese herbal medicine for diabetic peripheral neuropathy: an updated meta-analysis of 10 high-quality randomized controlled studies.PLoS One. 2013 Oct 16;8(10):e76113. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0076113. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24146822 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Is acupoint injection the optimal way to administer mecobalamin for diabetic peripheral neuropathy? A meta-analysis and trial sequential analysis.Front Neurol. 2023 Oct 18;14:1186420. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2023.1186420. eCollection 2023. Front Neurol. 2023. PMID: 37920836 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Acupuncture on Diabetic Neuropathy: A Narrative Review.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Aug 9;22(16):8575. doi: 10.3390/ijms22168575. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34445280 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Impact of acuinjection at ST36 on leg movements, their associated respiratory events, and electroencephalographic arousals in patients with obstructive sleep apnea: A case series.Medicine (Baltimore). 2025 Jul 25;104(30):e43401. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000043401. Medicine (Baltimore). 2025. PMID: 40725949 Free PMC article.
-
Acupuncture therapy on postoperative nausea and vomiting in abdominal operation: A Bayesian network meta analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2020 Jun 5;99(23):e20301. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000020301. Medicine (Baltimore). 2020. PMID: 32501976 Free PMC article.
-
Acupuncture for the Relief of Chronic Pain: A Synthesis of Systematic Reviews.Medicina (Kaunas). 2019 Dec 24;56(1):6. doi: 10.3390/medicina56010006. Medicina (Kaunas). 2019. PMID: 31878346 Free PMC article.
References
-
- International Diabetes Federation. IDF Diabetes Atlas Eighth edition 2017. Online document at: https://www.idf.org/our-activities/advocacy-awareness/resources-and-tool..., accessed January10, 2018
-
- Xu Y, Wang L, He J, et al. . Prevalence and control of diabetes in Chinese adults. JAMA 2013;310:948–959 - PubMed
-
- Tesfaye S, Selvarajah D. Advances in the epidemiology, pathogenesis and management of diabetic peripheral neuropathy. Diabetes Metab Res Rev 2012;28:8–14 - PubMed
-
- Boulton AJ, Vinik AI, Arezzo JC, et al. . Diabetic neuropathies: A statement by the American Diabetes Association. Diabetes Care 2005;28:956–962 - PubMed
-
- Tesfaye S, Vileikyte L, Rayman G, et al. . Painful diabetic peripheral neuropathy: Consensus recommendations on diagnosis, assessment and management. Diabetes Metab Res Rev 2011;27:629–638 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical