Diffusion-weighted imaging in rectal cancer: current applications and future perspectives
- PMID: 30433814
- PMCID: PMC6540856
- DOI: 10.1259/bjr.20180655
Diffusion-weighted imaging in rectal cancer: current applications and future perspectives
Abstract
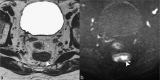
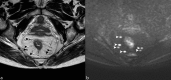
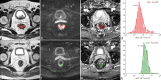
This review summarizes current applications and clinical utility of diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) for rectal cancer and in addition provides a brief overview of more recent developments (including intravoxel incoherent motion imaging, diffusion kurtosis imaging, and novel postprocessing tools) that are still in more early stages of research. More than 140 papers have been published in the last decade, during which period the use of DWI have slowly moved from mainly qualitative (visual) image interpretation to increasingly advanced methods of quantitative analysis. So far, the largest body of evidence exists for assessment of tumour response to neoadjuvant treatment. In this setting, particularly the benefit of DWI for visual assessment of residual tumour in post-radiation fibrosis has been established and is now increasingly adopted in clinics. Quantitative DWI analysis (mainly the apparent diffusion coefficient) has potential, both for response prediction as well as for tumour prognostication, but protocols require standardization and results need to be prospectively confirmed on larger scale. The role of DWI for further clinical tumour and nodal staging is less well-defined, although there could be a benefit for DWI to help detect lymph nodes. Novel methods of DWI analysis and post-processing are still being developed and optimized; the clinical potential of these tools remains to be established in the upcoming years.
Figures
References
-
- Beets-Tan RGH , Lambregts DMJ , Maas M , Bipat S , Barbaro B , Curvo-Semedo L , et al. . Magnetic resonance imaging for clinical management of rectal cancer: Updated recommendations from the 2016 European society of gastrointestinal and abdominal radiology (ESGAR) consensus meeting . Eur Radiol 2018. ; 28 : 1465 – 75 . doi: 10.1007/s00330-017-5026-2 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Soyer P , Lagadec M , Sirol M , Dray X , Duchat D , Vignaud A , et al. . Free-breathing diffusion-weighted single-shot echoplanar MR imaging using parallel imaging (GRAPPA 2) and high b value for the detection of primary rectal adenocarcinoma . Cancer Imaging 2010. ; 10 : 32 – 9 . doi: 10.1102/1470-7330.2010.0011 - DOI - PMC - PubMed

