Heterologous Hsp90 promotes phenotypic diversity through network evolution
- PMID: 30439936
- PMCID: PMC6264905
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pbio.2006450
Heterologous Hsp90 promotes phenotypic diversity through network evolution
Abstract
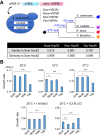
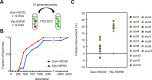
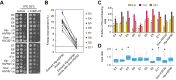
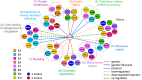
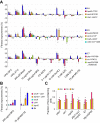
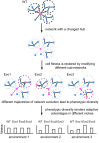
Biological processes in living cells are often carried out by gene networks in which signals and reactions are integrated through network hubs. Despite their functional importance, it remains unclear to what extent network hubs are evolvable and how alterations impact long-term evolution. We investigated these issues using heat shock protein 90 (Hsp90), a central hub of proteostasis networks. When native Hsp90 in Saccharomyces cerevisiae cells was replaced by the ortholog from hypersaline-tolerant Yarrowia lipolytica that diverged from S. cerevisiae about 270 million years ago, the cells exhibited improved growth in hypersaline environments but compromised growth in others, indicating functional divergence in Hsp90 between the two yeasts. Laboratory evolution shows that evolved Y. lipolytica-HSP90-carrying S. cerevisiae cells exhibit a wider range of phenotypic variation than cells carrying native Hsp90. Identified beneficial mutations are involved in multiple pathways and are often pleiotropic. Our results show that cells adapt to a heterologous Hsp90 by modifying different subnetworks, facilitating the evolution of phenotypic diversity inaccessible to wild-type cells.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

Comment in
-
Network hubs affect evolvability.PLoS Biol. 2019 Jan 30;17(1):e3000111. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.3000111. eCollection 2019 Jan. PLoS Biol. 2019. PMID: 30699103 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hartwell LH, Hopfield JJ, Leibler S, Murray AW. From molecular to modular cell biology. Nature. 1999;402(6761 Suppl):C47–52. 10.1038/35011540 . - DOI - PubMed
-
- Barabasi AL, Oltvai ZN. Network biology: understanding the cell's functional organization. Nat Rev Genet. 2004;5(2):101–13. Epub 2004/01/22. 10.1038/nrg1272 [pii]. . - DOI - PubMed
-
- Eisenberg D, Marcotte EM, Xenarios I, Yeates TO. Protein function in the post-genomic era. Nature. 2000;405(6788):823–6. 10.1038/35015694 . - DOI - PubMed
-
- Proulx SR, Promislow DE, Phillips PC. Network thinking in ecology and evolution. Trends Ecol Evol. 2005;20(6):345–53. 10.1016/j.tree.2005.04.004 . - DOI - PubMed
-
- Jeong H, Mason SP, Barabasi AL, Oltvai ZN. Lethality and centrality in protein networks. Nature. 2001;411(6833):41–2. Epub 2001/05/03. 10.1038/35075138 [pii]. . - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

