De novo biosynthesis of myricetin, kaempferol and quercetin in Streptomyces albus and Streptomyces coelicolor
- PMID: 30440014
- PMCID: PMC6237366
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0207278
De novo biosynthesis of myricetin, kaempferol and quercetin in Streptomyces albus and Streptomyces coelicolor
Abstract
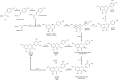
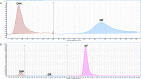
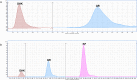
Flavonols are a flavonoid subfamily widely distributed in plants, including several ones of great importance in human and animal diet (apple, tomato, broccoli, onion, beans, tea). These polyphenolic nutraceuticals exert potent antimicrobial (membrane potential disruptors), antioxidant (free-radical scavengers), pharmacokinetic (CYP450 modulators), anti-inflammatory (lipoxygenase inhibitors), antiangiogenic (VEGF inhibitors) and antitumor (cyclin inhibitors) activities. Biotechnological production of these nutraceuticals, for example via heterologous biosynthesis in industrial actinomycetes, is favored since in plants these polyphenols appear as inactive glycosylated derivatives, in low concentrations or as part of complex mixtures with other polyphenolic compounds. In this work, we describe the de novo biosynthesis of three important flavonols, myricetin, kaempferol and quercetin, in the industrially relevant actinomycetes Streptomyces coelicolor and S. albus. De novo biosynthesis of kaempferol, myricetin and quercetin in actinomycetes has not been described before.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

Similar articles
-
De novo biosynthesis of garbanzol and fustin in Streptomyces albus based on a potential flavanone 3-hydroxylase with 2-hydroxylase side activity.Microb Biotechnol. 2021 Sep;14(5):2009-2024. doi: 10.1111/1751-7915.13874. Epub 2021 Jul 3. Microb Biotechnol. 2021. PMID: 34216097 Free PMC article.
-
Flavonoid (myricetin, quercetin, kaempferol, luteolin, and apigenin) content of edible tropical plants.J Agric Food Chem. 2001 Jun;49(6):3106-12. doi: 10.1021/jf000892m. J Agric Food Chem. 2001. PMID: 11410016
-
Effects of nitrogen supply on flavonol glycoside biosynthesis and accumulation in tea leaves (Camellia sinensis).Plant Physiol Biochem. 2019 May;138:48-57. doi: 10.1016/j.plaphy.2019.02.017. Epub 2019 Feb 22. Plant Physiol Biochem. 2019. PMID: 30849677
-
Increasing antioxidant levels in tomatoes through modification of the flavonoid biosynthetic pathway.J Exp Bot. 2002 Oct;53(377):2099-106. doi: 10.1093/jxb/erf044. J Exp Bot. 2002. PMID: 12324533 Review.
-
Molecular Pathways Involved in the Anti-Cancer Activity of Flavonols: A Focus on Myricetin and Kaempferol.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Apr 16;23(8):4411. doi: 10.3390/ijms23084411. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35457229 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Untargeted Metabolomics Profiling Reveals Beneficial Changes in Milk of Sows Supplemented with Fermented Compound Chinese Medicine Feed Additive.Animals (Basel). 2022 Oct 21;12(20):2879. doi: 10.3390/ani12202879. Animals (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36290264 Free PMC article.
-
Synthetic spatial patterning in bacteria: advances based on novel diffusible signals.Microb Biotechnol. 2022 Jun;15(6):1685-1694. doi: 10.1111/1751-7915.13979. Epub 2021 Nov 29. Microb Biotechnol. 2022. PMID: 34843638 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Reconstruction of a Genome-Scale Metabolic Model of Streptomyces albus J1074: Improved Engineering Strategies in Natural Product Synthesis.Metabolites. 2021 May 11;11(5):304. doi: 10.3390/metabo11050304. Metabolites. 2021. PMID: 34064751 Free PMC article.
-
Enhancing systemic resistance in faba bean (Vicia faba L.) to Bean yellow mosaic virus via soil application and foliar spray of nitrogen-fixing Rhizobium leguminosarum bv. viciae strain 33504-Alex1.Front Plant Sci. 2022 Aug 2;13:933498. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.933498. eCollection 2022. Front Plant Sci. 2022. PMID: 35982695 Free PMC article.
-
Microbial production of nutraceuticals: Metabolic engineering interventions in phenolic compounds, poly unsaturated fatty acids and carotenoids synthesis.J Food Sci Technol. 2023 Aug;60(8):2092-2104. doi: 10.1007/s13197-022-05482-5. Epub 2022 Jun 18. J Food Sci Technol. 2023. PMID: 37273565 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Li A, Li S, Zhang Y, Xu X, Chen Y, Li H. Resources and Biological Activities of Natural Polyphenols. Nutrients. 2014;6: 6020–6047. 10.3390/nu6126020 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Manach C, Scalbert A, Morand C, Rémésy C, Jiménez L. Polyphenols: Food sources and bioavailability. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition. 2004. pp. 727–747. 10.1093/ajcn/79.5.727 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Tsao R. Chemistry and biochemistry of dietary polyphenols. Nutrients. 2010;2: 1231–1246. 10.3390/nu2121231 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- González-Vallinas M, González-Castejón M, Rodríguez-Casado A, Ramírez de Molina A. Dietary phytochemicals in cancer prevention and therapy: A complementary approach with promising perspectives. Nutr Rev. 2013;71: 585–599. 10.1111/nure.12051 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Chaudhuri S, Sengupta B, Taylor J, Pahari BP, Sengupta PK. Interactions of Dietary Flavonoids with Proteins: Insights from Fluorescence Spectroscopy and Other Related Biophysical Studies. Curr Drug Metab. 2013;14: 491–503. 10.2174/1389200211314040011 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

