Origins of truncated supplementary capsid proteins in rAAV8 vectors produced with the baculovirus system
- PMID: 30440025
- PMCID: PMC6237368
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0207414
Origins of truncated supplementary capsid proteins in rAAV8 vectors produced with the baculovirus system
Abstract
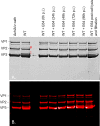
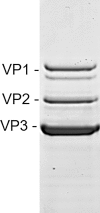
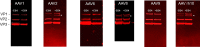
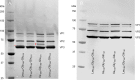
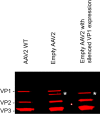
The ability to produce large quantities of recombinant Adeno-Associated Virus (rAAV) vectors is an important factor for the development of gene therapy-based medicine. The baculovirus/insect cell expression system is one of the major systems for large scale rAAV production. So far, most technological developments concerned the optimization of the AAV rep and cap genes in order to be expressed correctly in a heterologous system. However, the effect of the baculovirus infection on the production of rAAV has not been examined in detail. In this study we show that the baculoviral cathepsin (v-CATH) protease is active on several (but not all) rAAV serotypes, leading to a partial degradation of VP1/VP2 proteins. Subsequently, we identified the principal v-CATH cleavage site in the rAAV8 capsid proteins and demonstrated that the cleavage is highly specific. The proteolytic degradation of VP1/VP2 AAV capsid proteins reduces the infectivity of rAAV vectors but can be prevented by the use of a baculovirus vector with a deletion of the chiA/v-cath locus or by addition of the E64 protease inhibitor during production. Moreover, the codon optimization of AAV cap performed for several serotypes and originally aimed at the removal of potential alternative initiation codons, resulted in incorporation of additional forms of truncated VP1 into the rAAV capsids.
Conflict of interest statement
LG is currently employed by Finvector. AS is currently employed by Synpromics Ltd. Lionel Galibert, Monique M. van Oers and Otto-Wilhelm Merten are inventors of patent WO2013014294 related to the current work. This does not alter our adherence to PLOS ONE policies on sharing data and materials.
Figures



Similar articles
-
A Lac Repressor-Inducible Baculovirus Expression Vector for Controlling Adeno-Associated Virus Capsid Ratios.Viruses. 2023 Dec 28;16(1):51. doi: 10.3390/v16010051. Viruses. 2023. PMID: 38257750 Free PMC article.
-
OneBac 2.0: Sf9 Cell Lines for Production of AAV1, AAV2, and AAV8 Vectors with Minimal Encapsidation of Foreign DNA.Hum Gene Ther Methods. 2017 Feb;28(1):15-22. doi: 10.1089/hgtb.2016.164. Hum Gene Ther Methods. 2017. PMID: 28125901 Free PMC article.
-
Improved Genome Packaging Efficiency of Adeno-associated Virus Vectors Using Rep Hybrids.J Virol. 2021 Sep 9;95(19):e0077321. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00773-21. Epub 2021 Jul 21. J Virol. 2021. PMID: 34287038 Free PMC article.
-
Custom adeno-associated virus capsids: the next generation of recombinant vectors with novel tropism.Hum Gene Ther. 2005 Apr;16(4):408-16. doi: 10.1089/hum.2005.16.408. Hum Gene Ther. 2005. PMID: 15871672 Review.
-
[Recombinant adeno-associated virus vector related impurities].Sheng Wu Gong Cheng Xue Bao. 2011 May;27(5):717-23. Sheng Wu Gong Cheng Xue Bao. 2011. PMID: 21845838 Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
Development of Versatile and Flexible Sf9 Packaging Cell Line-Dependent OneBac System for Large-Scale Recombinant Adeno-Associated Virus Production.Hum Gene Ther Methods. 2019 Oct;30(5):172-183. doi: 10.1089/hgtb.2019.123. Hum Gene Ther Methods. 2019. PMID: 31566024 Free PMC article.
-
A robust and flexible baculovirus-insect cell system for AAV vector production with improved yield, capsid ratios and potency.Mol Ther Methods Clin Dev. 2024 Mar 4;32(2):101228. doi: 10.1016/j.omtm.2024.101228. eCollection 2024 Jun 13. Mol Ther Methods Clin Dev. 2024. PMID: 38524756 Free PMC article.
-
Bombyx mori Pupae Efficiently Produce Recombinant AAV2/HBoV1 Vectors with a Bombyx mori Nuclear Polyhedrosis Virus Expression System.Viruses. 2021 Apr 18;13(4):704. doi: 10.3390/v13040704. Viruses. 2021. PMID: 33919645 Free PMC article.
-
Scarless Baculovirus Genome Editing Using Lambda-Red Recombineering in E. coli.Methods Mol Biol. 2024;2829:109-126. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-3961-0_8. Methods Mol Biol. 2024. PMID: 38951330
-
Characterizing the Content and Structure of AAV Capsids by Size Exclusion Chromatography and Orbitrap-Based Charge Detection-Mass Spectrometry.J Am Soc Mass Spectrom. 2025 Aug 6;36(8):1659-1668. doi: 10.1021/jasms.5c00074. Epub 2025 Jun 26. J Am Soc Mass Spectrom. 2025. PMID: 40568774 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Urabe M, Ding C, Kotin RM. Insect cells as a factory to produce adeno-associated virus type 2 vectors. Hum Gene Ther. 2002;13: 1935–1943. 10.1089/10430340260355347 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Smith RH, Levy JR, Kotin RM. A simplified baculovirus-AAV expression vector system coupled with one-step affinity purification yields high-titer rAAV stocks from insect cells. Mol Ther. Nature Publishing Group; 2009;17: 1888–1896. 10.1038/mt.2009.128 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Galibert L, Merten O-W. Latest developments in the large-scale production of adeno-associated virus vectors in insect cells toward the treatment of neuromuscular diseases. J Invertebr Pathol. Elsevier Inc.; 2011;107 Suppl: S80–S93. 10.1016/j.jip.2011.05.008 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Cecchini S, Virag T, Kotin RM. Reproducible high yields of recombinant adeno-associated virus produced using invertebrate cells in 0.02- to 200-liter cultures. Hum Gene Ther. 2011;22: 1021–1030. 10.1089/hum.2010.250 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Slack JM, Kuzio J, Faulkner P. Characterization of v-cath, a cathepsin L-like proteinase expressed by the baculovirus Autographa californica multiple nuclear polyhedrosis virus. J Gen Virol. 1995;76: 1091–1098. 10.1099/0022-1317-76-5-1091 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

