Impact of meropenem on Klebsiella pneumoniae metabolism
- PMID: 30440048
- PMCID: PMC6237392
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0207478
Impact of meropenem on Klebsiella pneumoniae metabolism
Abstract
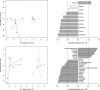
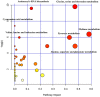
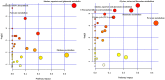
The aim of this study was to analyze the metabolome of several Klebsiella pneumoniae strains characterized by different resistance patterns. A total of 59 bacterial strains (27 carbapenemase-negative and 32 carbapenemase-positive) were included and their metabolic features were assessed in basal conditions. Moreover, 8 isolates (4 wild-type and 4 KPC-producers) were randomly selected to evaluate the impact of sub-lethal concentrations of meropenem on bacterial metabolism. The metabolomic analysis was performed by 1H-NMR spectroscopy both on filtered supernatants and cell lysates. A total of 40 and 20 molecules were quantified in the intracellular and the extracellular metabolome, respectively. While in basal conditions only five metabolites showed significant differences between carbapenemase-positive and negative strains, the use of meropenem had a profound impact on the whole bacterial metabolism. In the intracellular compartment, a reduction of different overflow metabolites and organic acids (e.g. formate, acetate, isobutyrate) was noticed, whereas, in the extracellular metabolome, the levels of several organic acids (e.g. succinate, acetate, formate, lactate) and amino acids (aspartate, threonine, lysine, alanine) were modified by meropenem stimulation. Interestingly, carbapenemase-positive and negative strains reacted differently to meropenem in terms of number and type of perturbed metabolites. In wild-type strains, meropenem had great impact on the metabolic pathways related to methane metabolism and alanine, aspartate and glutamate metabolism, whereas in KPC-producers the effect was predominant on pyruvate metabolism. The knowledge about the bacterial metabolic profiles could help to set up innovative diagnostic methods and new antimicrobial strategies to fight the global crisis against carbapenemase-positive K. pneumoniae.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- Tzouvelekis LS, Markogiannakis A, Psichogiou M, Tassios PT, Daikos GL. Carbapenemases in Klebsiella pneumoniae and other Enterobacteriaceae: an evolving crisis of global dimensions. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2012;25: 682–707. 10.1128/CMR.05035-11 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control. Antimicrobial resistance surveillance in Europe 2014. Annual Report of the European Antimicrobial Resistance Surveillance Network (EARS-Net). Stockholm: ECDC; 2015.
-
- Giani T, Pini B, Arena F, Conte V, Bracco S, Migliavacca R, et al. Epidemic diffusion of KPC carbapenemase-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae in Italy: results of the first countrywide survey, 15 May to 30 June 2011. Euro Surveill. 2013; 18: pii = 20489. - PubMed
-
- Grundmann H, Livermore DM, Giske CG, Canton R, Rossolini GM, Campos J, et al. Carbapenem-non-susceptible Enterobacteriaceae in Europe: conclusions from a meeting of national experts. Euro Surveill. 2010;15: pii = 19711. - PubMed
-
- Diene SM, Rolain JM. Carbapenemase genes and genetic platforms in Gram-negative bacilli: Enterobacteriaceae, Pseudomonas and Acinetobacter species. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2014;20: 831–838. 10.1111/1469-0691.12655 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

