Pharmacological modulation of mitochondrial ion channels
- PMID: 30440086
- PMCID: PMC6887689
- DOI: 10.1111/bph.14544
Pharmacological modulation of mitochondrial ion channels
Abstract
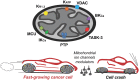
The field of mitochondrial ion channels has undergone a rapid development during the last three decades, due to the molecular identification of some of the channels residing in the outer and inner membranes. Relevant information about the function of these channels in physiological and pathological settings was gained thanks to genetic models for a few, mitochondria-specific channels. However, many ion channels have multiple localizations within the cell, hampering a clear-cut determination of their function by pharmacological means. The present review summarizes our current knowledge about the ins and outs of mitochondrial ion channels, with special focus on the channels that have received much attention in recent years, namely, the voltage-dependent anion channels, the permeability transition pore (also called mitochondrial megachannel), the mitochondrial calcium uniporter and some of the inner membrane-located potassium channels. In addition, possible strategies to overcome the difficulties of specifically targeting mitochondrial channels versus their counterparts active in other membranes are discussed, as well as the possibilities of modulating channel function by small peptides that compete for binding with protein interacting partners. Altogether, these promising tools along with large-scale chemical screenings set up to identify new, specific channel modulators will hopefully allow us to pinpoint the actual function of most mitochondrial ion channels in the near future and to pharmacologically affect important pathologies in which they are involved, such as neurodegeneration, ischaemic damage and cancer. LINKED ARTICLES: This article is part of a themed section on Mitochondrial Pharmacology: Featured Mechanisms and Approaches for Therapy Translation. To view the other articles in this section visit http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/bph.v176.22/issuetoc.
© 2018 The British Pharmacological Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Abdoul‐Azize S, Buquet C, Vannier JP, Dubus I (2016). Pyr3, a TRPC3 channel blocker, potentiates dexamethasone sensitivity and apoptosis in acute lymphoblastic leukemia cells by disturbing Ca(2+) signaling, mitochondrial membrane potential changes and reactive oxygen species production. Eur J Pharmacol 784: 90–98. - PubMed
-
- Aissaoui D, Mlayah‐Bellalouna S, Jebali J, Abdelkafi‐Koubaa Z, Souid S, Moslah W et al (2018). Functional role of Kv1.1 and Kv1.3 channels in the neoplastic progression steps of three cancer cell lines, elucidated by scorpion peptides. Int J Biol Macromol 111: 1146–1155. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

