Spatial Patterning from an Integrated Wnt/β-catenin and Notch/Delta Gene Circuit
- PMID: 30441469
- PMCID: PMC7081632
- DOI: 10.1109/EMBC.2018.8513462
Spatial Patterning from an Integrated Wnt/β-catenin and Notch/Delta Gene Circuit
Abstract
Classically, the Wnt/β-catenin and Notch /Delta signaling pathways were thought to operate through separate mechanisms, performing distinct roles in tissue patterning. However, it has been shown that b-catenin activates transcription of Hesl, a signaling intermediate in the Notch /Delta pathway that controls its lateral inhibition mechanism. To investigate this non-canonical crosstalk mechanism, a new gene circuit, integrating the two pathways, is proposed and simulated in two-cell and multi-cell environments. This model also captures both Paneth cell- mediated and mesenchymal Wnt production. The simulations verify that the gene circuit is temporally bistable and capable of forming a pattern on a multi-cell grid. Last, the model exhibits a bifurcation based on the steady state concentration of Wnt and the relative amount of control b-catenin has over the Hesl promoter, providing a possible mechanism to explain why a homogeneous population of transit amplifying cells is observed directly above the more diverse stem niche.
Figures

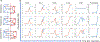
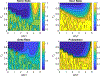
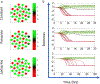
References
-
- Snippert HJ et al. , “Intestinal Crypt Homeostasis Results from Neutral Competition between Symmetrically Dividing Lgr5 Stem Cells,” Cell, vol. 143, no. 1, pp. 134–144, October 2010. - PubMed
-
- Barker N, “Adult intestinal stem cells: critical drivers of epithelial homeostasis and regeneration,” Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol, vol. 15, no. 1, pp. 19–33, January 2014. - PubMed
-
- Sato T et al. , “Single Lgr5 stem cells build crypt–villus structures in vitro without a mesenchymal niche,” Nature, vol. 459, no. 7244, pp. 262–265, May 2009. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
