Breast Cancer: An Examination of the Potential of ACKR3 to Modify the Response of CXCR4 to CXCL12
- PMID: 30441765
- PMCID: PMC6274818
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms19113592
Breast Cancer: An Examination of the Potential of ACKR3 to Modify the Response of CXCR4 to CXCL12
Erratum in
-
Correction: del Molino del Barrio et al. Breast Cancer: An Examination of the Potential of ACKR3 to Modify the Response of CXCR4 to CXCL12. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3592.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Dec 4;24(23):17108. doi: 10.3390/ijms242317108. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38069447 Free PMC article.
Abstract
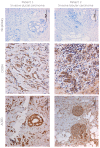
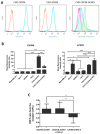
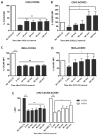
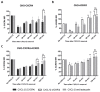
Upon binding with the chemokine CXCL12, the chemokine receptor CXCR4 has been shown to promote breast cancer progression. This process, however, can be affected by the expression of the atypical chemokine receptor ACKR3. Given ACKR3's ability to form heterodimers with CXCR4, we investigated how dual expression of both receptors differed from their lone expression in terms of their signalling pathways. We created single and double CXCR4 and/or ACKR3 Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) cell transfectants. ERK and Akt phosphorylation after CXCL12 stimulation was assessed and correlated with receptor internalization. Functional consequences in cell migration and proliferation were determined through wound healing assays and calcium flux. Initial experiments showed that CXCR4 and ACKR3 were upregulated in primary breast cancer and that CXCR4 and ACKR3 could form heterodimers in transfected CHO cells. This co-expression modified CXCR4's Akt activation after CXCL12's stimulation but not ERK phosphorylation (p < 0.05). To assess this signalling disparity, receptor internalization was assessed and it was observed that ACKR3 was recycled to the surface whilst CXCR4 was degraded (p < 0.01), a process that could be partially inhibited with a proteasome inhibitor (p < 0.01). Internalization was also assessed with the ACKR3 agonist VUF11207, which caused both CXCR4 and ACKR3 to be degraded after internalization (p < 0.05 and p < 0.001), highlighting its potential as a dual targeting drug. Interestingly, we observed that CXCR4 but not ACKR3, activated calcium flux after CXCL12 stimulation (p < 0.05) and its co-expression could increase cellular migration (p < 0.01). These findings suggest that both receptors can signal through ERK and Akt pathways but co-expression can alter their kinetics and internalization pathways.
Keywords: ACKR3; CXCR4; CXCR7; chemokines; heterodimerization; metastasis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Greene F.L., Page D.L., Fleming I.D., Fritz A.G., Balch C.M., Haller D.G., Morrow M. AJCC Cancer Staging Manual. 6th ed. Springer; New York, NY, USA: 2002. Breast; pp. 223–240.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

