Role of Ca2+ in Mediating Plant Responses to Extracellular ATP and ADP
- PMID: 30441766
- PMCID: PMC6274673
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms19113590
Role of Ca2+ in Mediating Plant Responses to Extracellular ATP and ADP
Abstract
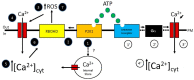
Among the most recently discovered chemical regulators of plant growth and development are extracellular nucleotides, especially extracellular ATP (eATP) and extracellular ADP (eADP). Plant cells release ATP into their extracellular matrix under a variety of different circumstances, and this eATP can then function as an agonist that binds to a specific receptor and induces signaling changes, the earliest of which is an increase in the concentration of cytosolic calcium ([Ca2+]cyt). This initial change is then amplified into downstream-signaling changes that include increased levels of reactive oxygen species and nitric oxide, which ultimately lead to major changes in the growth rate, defense responses, and leaf stomatal apertures of plants. This review presents and discusses the evidence that links receptor activation to increased [Ca2+]cyt and, ultimately, to growth and diverse adaptive changes in plant development. It also discusses the evidence that increased [Ca2+]cyt also enhances the activity of apyrase (nucleoside triphosphate diphosphohydrolase) enzymes that function in multiple subcellular locales to hydrolyze ATP and ADP, and thus limit or terminate the effects of these potent regulators.
Keywords: NADPH oxidase; apyrase; calmodulin; nitric oxide; reactive oxygen species.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

