Transport of Apolipoprotein B-Containing Lipoproteins through Endothelial Cells Is Associated with Apolipoprotein E-Carrying HDL-Like Particle Formation
- PMID: 30441770
- PMCID: PMC6274886
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms19113593
Transport of Apolipoprotein B-Containing Lipoproteins through Endothelial Cells Is Associated with Apolipoprotein E-Carrying HDL-Like Particle Formation
Abstract
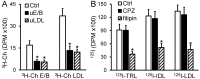
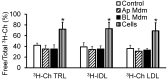
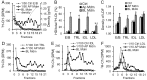
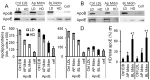
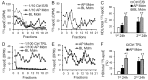
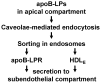
Passage of apolipoprotein B-containing lipoproteins (apoB-LPs), i.e., triglyceride-rich lipoproteins (TRLs), intermediate-density lipoproteins (IDLs), and low-density lipoproteins (LDLs), through the endothelial monolayer occurs in normal and atherosclerotic arteries. Among these lipoproteins, TRLs and IDLs are apoE-rich apoB-LPs (E/B-LPs). Recycling of TRL-associated apoE has been shown to form apoE-carrying high-density lipoprotein (HDL)-like (HDLE) particles in many types of cells. The current report studied the formation of HDLE particles by transcytosis of apoB-LPs through mouse aortic endothelial cells (MAECs). Our data indicated that passage of radiolabeled apoB-LPs, rich or poor in apoE, through the MAEC monolayer is inhibited by filipin and unlabeled competitor lipoproteins, suggesting that MAECs transport apoB-LPs via a caveolae-mediated pathway. The cholesterol and apoE in the cell-untreated E/B-LPs, TRLs, IDLs, and LDLs distributed primarily in the low-density (LD) fractions (d ≤ 1.063). A substantial portion of the cholesterol and apoE that passed through the MAEC monolayer was allotted into the high-density (HD) (d > 1.063) fractions. In contrast, apoB was detectable only in the LD fractions before or after apoB-LPs were incubated with the MAEC monolayer, suggesting that apoB-LPs pass through the MAEC monolayer in the forms of apoB-containing LD particles and apoE-containing HD particles.
Keywords: apolipoprotein B-containing lipoprotein; apolipoprotein E; high-density lipoprotein formation; mouse aortic endothelial cells; transendothelial transport.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Apolipoprotein A-I Inhibits Transendothelial Transport of Apolipoprotein B-Carrying Lipoproteins and Enhances Its Associated High-Density Lipoprotein Formation.J Vasc Res. 2022;59(5):275-287. doi: 10.1159/000525259. Epub 2022 Jun 27. J Vasc Res. 2022. PMID: 35760057 Free PMC article.
-
Overexpression of hepatic lipase in transgenic mice decreases apolipoprotein B-containing and high density lipoproteins. Evidence that hepatic lipase acts as a ligand for lipoprotein uptake.J Biol Chem. 1998 Jan 23;273(4):1896-903. doi: 10.1074/jbc.273.4.1896. J Biol Chem. 1998. PMID: 9442022
-
Structural peculiarities of the binding of very low density lipoproteins and low density lipoproteins to the LDL receptor in hypertriglyceridemia: role of apolipoprotein E.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2000 Feb 24;1484(1):29-40. doi: 10.1016/s1388-1981(99)00197-3. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2000. PMID: 10685028
-
[THE BECOMING IN PHYLOGENESIS OF TRANSFER IN INTERCELLULAR MEDIUM AND ACTIVE ABSORPTION OF POLYENOIC FATTY ACIDS BY CELLS SEQUENTIALLY OF HIGH DENSITY LIPOPROTEINS, LOW DENSITY LIPOPROTEINS AND HIGH DENSITY APOE-LIPOPROTEINS].Klin Lab Diagn. 2015 Jun;60(6):4-14. Klin Lab Diagn. 2015. PMID: 26466444 Review. Russian.
-
Hepatic synthesis of lipoproteins and apolipoproteins.Semin Liver Dis. 1992 Nov;12(4):364-72. doi: 10.1055/s-2008-1040406. Semin Liver Dis. 1992. PMID: 1465621 Review.
Cited by
-
Intracellular Membrane Transport in Vascular Endothelial Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Mar 17;24(6):5791. doi: 10.3390/ijms24065791. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36982865 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Apolipoprotein A-I Inhibits Transendothelial Transport of Apolipoprotein B-Carrying Lipoproteins and Enhances Its Associated High-Density Lipoprotein Formation.J Vasc Res. 2022;59(5):275-287. doi: 10.1159/000525259. Epub 2022 Jun 27. J Vasc Res. 2022. PMID: 35760057 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Simvastatin on Augmentation Index Are Transient: Outcomes From a Randomized Controlled Trial.J Am Heart Assoc. 2019 Oct 15;8(20):e009792. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.118.009792. Epub 2019 Oct 12. J Am Heart Assoc. 2019. PMID: 31607205 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Protein corona and exosomes: new challenges and prospects.Cell Commun Signal. 2023 Mar 27;21(1):64. doi: 10.1186/s12964-023-01089-1. Cell Commun Signal. 2023. PMID: 36973780 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Foley E.M., Esko J.D. Hepatic heparan sulfate proteoglycans and endocytic clearance of triglyceride-rich lipoproteins. Prog. Mol. Biol. Transl. Sci. 2010;93:213–233. - PubMed
-
- Feingold K.R., Grunfeld C. Introduction to Lipids and Lipoproteins. In: De Groot L.J., Chrousos G., Dungan K., Feingold K.R., Grossman A., Hershman J.M., Koch C., Korbonits M., McLachlan R., New M., et al., editors. Endotext. MDText.com, Inc.; South Dartmouth, MA, USA: 2000.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

