The H₂S Donor GYY4137 Stimulates Reactive Oxygen Species Generation in BV2 Cells While Suppressing the Secretion of TNF and Nitric Oxide
- PMID: 30441775
- PMCID: PMC6278327
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules23112966
The H₂S Donor GYY4137 Stimulates Reactive Oxygen Species Generation in BV2 Cells While Suppressing the Secretion of TNF and Nitric Oxide
Abstract
GYY4137 is a hydrogen sulfide (H₂S) donor that has been shown to act in an anti-inflammatory manner in vitro and in vivo. Microglial cells are among the major players in immunoinflammatory, degenerative, and neoplastic disorders of the central nervous system, including multiple sclerosis, Parkinson's disease, Alzheimer's disease, and glioblastoma multiforme. So far, the effects of GYY4137 on microglial cells have not been thoroughly investigated. In this study, BV2 microglial cells were stimulated with interferon-gamma and lipopolysaccharide and treated with GYY4137. The agent did not influence the viability of BV2 cells in concentrations up to 200 μM. It inhibited tumor necrosis factor but not interleukin-6 production. Expression of CD40 and CD86 were reduced under the influence of the donor. The phagocytic ability of BV2 cells and nitric oxide production were also affected by the agent. Surprisingly, GYY4137 upregulated generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) by BV2 cells. The effect was mimicked by another H₂S donor, Na₂S, and it was not reproduced in macrophages. Our results demonstrate that GYY4137 downregulates inflammatory properties of BV2 cells but increases their ability to generate ROS. Further investigation of this unexpected phenomenon is warranted.
Keywords: GYY4137; hydrogen sulfide; inflammation; microglia; reactive oxygen species.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
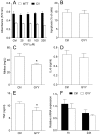
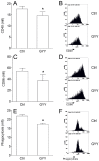
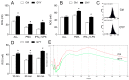

References
-
- Wallace J.L., Blackler R.W., Chan M.V., Da Silva G.J., Elsheikh W., Flannigan K.L., Gamaniek I., Manko A., Wang L., Motta J.-P., et al. Anti-inflammatory and cytoprotective actions of hydrogen sulfide: translation to therapeutics. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2015;22:398–410. doi: 10.1089/ars.2014.5901. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Xue X., Bian J.-S. Neuroprotective effects of hydrogen sulfide in Parkinson’s disease animal models: methods and protocols. Methods Enzymol. 2015;554:169–186. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

