Tumidulin, a Lichen Secondary Metabolite, Decreases the Stemness Potential of Colorectal Cancer Cells
- PMID: 30441806
- PMCID: PMC6278574
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules23112968
Tumidulin, a Lichen Secondary Metabolite, Decreases the Stemness Potential of Colorectal Cancer Cells
Abstract
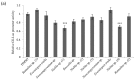
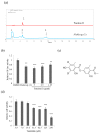
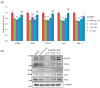
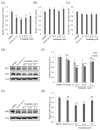
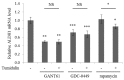
Lichens produce various unique chemicals that are used in the pharmaceutical industry. To screen for novel lichen secondary metabolites that inhibit the stemness potential of colorectal cancer cells, we tested acetone extracts of 11 lichen samples collected in Chile. Tumidulin, isolated from Niebla sp., reduced spheroid formation in CSC221, DLD1, and HT29 cells. In addition, mRNA expressions and protein levels of cancer stem markers aldehyde dehydrogenase-1 (ALDH1), cluster of differentiation 133 (CD133), CD44, Lgr5, and Musashi-1 were reduced after tumidulin treatment. Tumidulin decreased the transcriptional activity of the glioma-associated oncogene homolog zinc finger protein (Gli) promoter in reporter assays, and western blotting confirmed decreased Gli1, Gli2, and Smoothened (SMO) protein levels. Moreover, the tumidulin activity was not observed in the presence of Gli and SMO inhibitors. Together, these results demonstrate for the first time that tumidulin is a potent inhibitor of colorectal cancer cell stemness.
Keywords: colorectal cancer cells; lichen; oncogene; secondary metabolites; stemness potential; transcriptional regulation; tumidulin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Bhandari A., Woodhouse M., Gupta S. Colorectal cancer is a leading cause of cancer incidence and mortality among adults younger than 50 years in the USA: A SEER-based analysis with comparison to other young-onset cancers. J. Investig. Med. 2017;65:311–315. doi: 10.1136/jim-2016-000229. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

