SS1P Immunotoxin Induces Markers of Immunogenic Cell Death and Enhances the Effect of the CTLA-4 Blockade in AE17M Mouse Mesothelioma Tumors
- PMID: 30441807
- PMCID: PMC6265743
- DOI: 10.3390/toxins10110470
SS1P Immunotoxin Induces Markers of Immunogenic Cell Death and Enhances the Effect of the CTLA-4 Blockade in AE17M Mouse Mesothelioma Tumors
Abstract
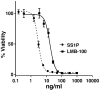
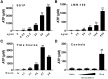
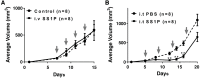
SS1P is an anti-mesothelin immunotoxin composed of a targeting antibody fragment genetically fused to a truncated fragment of Pseudomonas exotoxin A. Delayed responses reported in mesothelioma patients receiving SS1P suggest that anti-tumor immunity is induced. The goal of this study is to evaluate if SS1P therapy renders mesothelioma tumors more sensitive to cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated antigen 4 (CTLA-4) immune checkpoint blockade. We evaluated the ability of SS1P to induce adenosine triphosphate (ATP) secretion and calreticulin expression on the surface of AE17M mouse mesothelioma cells. Both properties are associated with immunogenic cell death. Furthermore, we treated these tumors with intra-tumoral SS1P and systemic CTLA-4. We found that SS1P increased the release of ATP from AE17M cells in a dose and time-dependent manner. In addition, SS1P induced calreticulin expression on the surface of AE17M cells. These results suggest that SS1P promotes immunogenic cell death and could sensitize tumors to anti-CTLA-4 based therapy. In mouse studies, we found that the combination of anti-CTLA-4 with intra-tumoral SS1P induced complete regressions in most mice and provided a statistically significant survival benefit compared to monotherapy. The surviving mice were protected from tumor re-challenge, indicating the development of anti-tumor immunity. These findings support the use of intra-tumoral SS1P in combination with anti-CTLA-4.
Keywords: ATP; Calreticulin; SS1P; anti-CTLA-4; immunogenic cell death; immunotherapy; immunotoxins; mesothelin; mesothelioma.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare no conflict of interest exists. The work was supported by the Intramural Research Program of the NIH, National Cancer Institute, Center for Cancer Research (Project ZO1 BC008753).
Figures
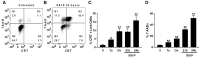

References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

