New treatments for the mucopolysaccharidoses: from pathophysiology to therapy
- PMID: 30442204
- PMCID: PMC6238257
- DOI: 10.1186/s13052-018-0564-z
New treatments for the mucopolysaccharidoses: from pathophysiology to therapy
Abstract
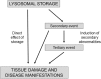
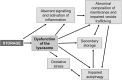
Enzyme replacement therapy is currently considered the standard of care for the treatment of mucopolysaccharidoses (MPS) type I, II, VI, and IV. This approach has shown substantial efficacy mainly on somatic symptoms of the patients, but no benefit was found for other clinical manifestations, such as neurological involvement. New strategies are currently being tested to address these limitations, in particular to obtain sufficient therapeutic levels in the brain. Intrathecal delivery of recombinant enzymes or chimeric enzymes represent promising approaches in this respect. Further innovation will likely be introduced by the recent advancements in the knowledge of lysosomal biology and function. It is now clear that the clinical manifestations of MPS are not only the direct effects of storage, but also derive from a cascade of secondary events that lead to dysfunction of several cellular processes and pathways. Some of these pathways may represent novel therapeutic targets and allow for development of novel or adjunctive therapies for these disorders.
Keywords: Autophagy; Blood-brain barrier; Enzyme replacement therapy; Gene therapy; Mucopolysaccharidoses.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
References
-
- Ballabio A, Gieselmann V. Lysosomal disorders: from storage to cellular damage. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1793;2009:684–696. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

