Regulation of immune responses by E3 ubiquitin ligase Cbl-b
- PMID: 30442330
- PMCID: PMC6504630
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cellimm.2018.11.002
Regulation of immune responses by E3 ubiquitin ligase Cbl-b
Abstract
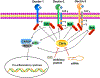
Casitas B lymphoma-b (Cbl-b), a RING finger E3 ubiquitin ligase, has been identified as a critical regulator of adaptive immune responses. Cbl-b is essential for establishing the threshold for T cell activation and regulating peripheral T cell tolerance through various mechanisms. Intriguingly, recent studies indicate that Cbl-b also modulates innate immune responses, and plays a key role in host defense to pathogens and anti-tumor immunity. These studies suggest that targeting Cbl-b may represent a potential therapeutic strategy for the management of human immune-related disorders such as autoimmune diseases, infections, tumors, and allergic airway inflammation. In this review, we summarize the latest developments regarding the roles of Cbl-b in innate and adaptive immunity, and immune-mediated diseases.
Keywords: Cbl-b; Immune-related disorders; Innate and adaptive immune responses; T cell tolerance; Ubiquitination.
Copyright © 2018 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Interest
The authors declare no competing interest.
Figures

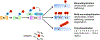


References
-
- Varshavsky A, The ubiquitin system, an immense realm, Annu Rev Biochem. 81(2012) 167–176. - PubMed
-
- Bhoj VG and Chen ZJ, Ubiquitylation in innate and adaptive immunity, Nature. 458 (2009) 430–437. - PubMed
-
- Keane MM, Rivero-Lezcano OM, Mitchell JA, Robbins KC and Lipkowitz S, Cloning and characterization of cbl-b: a SH3 binding protein with homology to the c-cbl proto-oncogene, Oncogene.10 (1995) 2367–2377. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

