The transcriptional coactivator WBP2 primes triple-negative breast cancer cells for responses to Wnt signaling via the JNK/Jun kinase pathway
- PMID: 30442712
- PMCID: PMC6311518
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.RA118.005796
The transcriptional coactivator WBP2 primes triple-negative breast cancer cells for responses to Wnt signaling via the JNK/Jun kinase pathway
Abstract
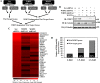
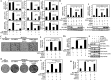
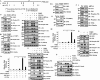
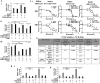
The transcriptional coactivator WW domain-binding protein 2 (WBP2) is an emerging oncogene and serves as a node between the signaling protein Wnt and other signaling molecules and pathways, including epidermal growth factor receptor, estrogen receptor/progesterone receptor, and the Hippo pathway. The upstream regulation of WBP2 is well-studied, but its downstream activity remains unclear. Here, we elucidated WBP2's role in triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC), in which Wnt signaling is predominantly activated. Using RNAi coupled with RNA-Seq and MS analyses to identify Wnt/WBP2- and WBP2-dependent targets in MDA-MB-231 TNBC cells, we found that WBP2 is required for the expression of a core set of genes in Wnt signaling. These included AXIN2, which was essential for Wnt/WBP2-mediated breast cancer growth and migration. WBP2 also regulated a much larger set of genes and proteins independently of Wnt, revealing that WBP2 primes cells to Wnt activity by up-regulating G protein pathway suppressor 1 (GPS1) and TRAF2- and NCK-interacting kinase (TNIK). GPS1 activated the c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK)/Jun pathway, resulting in a positive feedback loop with TNIK that mediated Wnt-induced AXIN2 expression. WBP2 promoted TNBC growth by integrating JNK with Wnt signaling, and its expression profoundly influenced the sensitivity of TNBC to JNK/TNIK inhibitors. In conclusion, WBP2 links JNK to Wnt signaling in TNBC. GPS1 and TNIK are constituents of a WBP2-initiated cascade that primes responses to Wnt ligands and are also important for TNBC biology. We propose that WBP2 is a potential drug target for JNK/TNIK-based precision medicine for managing TNBC.
Keywords: TNIK; WW domain–binding protein 2; Wnt signaling; axin; breast cancer; cell signaling; oncogene; precision medicine; therapy; transcription coactivator.
© 2018 Li et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest with the contents of this article
Figures



Similar articles
-
WBP2 promotes BTRC mRNA stability to drive migration and invasion in triple-negative breast cancer via NF-κB activation.Mol Oncol. 2022 Jan;16(2):422-446. doi: 10.1002/1878-0261.13048. Epub 2021 Aug 12. Mol Oncol. 2022. PMID: 34197030 Free PMC article.
-
WBP2 Downregulation Inhibits Proliferation by Blocking YAP Transcription and the EGFR/PI3K/Akt Signaling Pathway in Triple Negative Breast Cancer.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018;48(5):1968-1982. doi: 10.1159/000492520. Epub 2018 Aug 9. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018. PMID: 30092563
-
Hippo/MST blocks breast cancer by downregulating WBP2 oncogene expression via miRNA processor Dicer.Cell Death Dis. 2020 Aug 21;11(8):669. doi: 10.1038/s41419-020-02901-3. Cell Death Dis. 2020. PMID: 32820148 Free PMC article.
-
WW domain-binding protein 2: an adaptor protein closely linked to the development of breast cancer.Mol Cancer. 2017 Jul 19;16(1):128. doi: 10.1186/s12943-017-0693-9. Mol Cancer. 2017. PMID: 28724435 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Reciprocal Regulation of Hippo and WBP2 Signalling-Implications in Cancer Therapy.Cells. 2021 Nov 11;10(11):3130. doi: 10.3390/cells10113130. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34831354 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Signaling pathways and targeted therapies in lung squamous cell carcinoma: mechanisms and clinical trials.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2022 Oct 5;7(1):353. doi: 10.1038/s41392-022-01200-x. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2022. PMID: 36198685 Free PMC article. Review.
-
WBP2 inhibits microRNA biogenesis via interaction with the microprocessor complex.Life Sci Alliance. 2021 Jun 11;4(7):e202101038. doi: 10.26508/lsa.202101038. Print 2021 Jul. Life Sci Alliance. 2021. PMID: 34117091 Free PMC article.
-
Bioinformatics analysis of GPS1 expression and biological function in breast cancer.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2024 Jan 30;150(2):52. doi: 10.1007/s00432-023-05569-2. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38289496 Free PMC article.
-
Genomic analyses of PMBL reveal new drivers and mechanisms of sensitivity to PD-1 blockade.Blood. 2019 Dec 26;134(26):2369-2382. doi: 10.1182/blood.2019002067. Blood. 2019. PMID: 31697821 Free PMC article.
-
WBP2 promotes BTRC mRNA stability to drive migration and invasion in triple-negative breast cancer via NF-κB activation.Mol Oncol. 2022 Jan;16(2):422-446. doi: 10.1002/1878-0261.13048. Epub 2021 Aug 12. Mol Oncol. 2022. PMID: 34197030 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ferlay J., Soerjomataram I., Ervik M., Dikshit R., Eser S., Mathers C., Rebelo M., Parkin D., Forman D., and Bray F. (2013) GLOBOCAN 2012 v1.0. Cancer incidence and mortality worldwide: IARC CancerBase, 2014, IARC, Lyon, France - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

