Protein assemblies ejected directly from native membranes yield complexes for mass spectrometry
- PMID: 30442809
- PMCID: PMC6522346
- DOI: 10.1126/science.aau0976
Protein assemblies ejected directly from native membranes yield complexes for mass spectrometry
Erratum in
-
Erratum for the Report "Protein assemblies ejected directly from native membranes yield complexes for mass spectrometry" by D. S. Chorev, L. A. Baker, D. Wu, V. Beilsten-Edmands, S. L. Rouse, T. Zeev-Ben-Mordehai, C. Jiko, F. Samsudin, C. Gerle, S. Khalid, A. G. Stewart, S. J. Matthews, K. Grünewald, C. V. Robinson.Science. 2019 Apr 26;364(6438):eaax7485. doi: 10.1126/science.aax7485. Science. 2019. PMID: 31023898 No abstract available.
Abstract
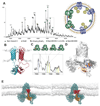
Membrane proteins reside in lipid bilayers and are typically extracted from this environment for study, which often compromises their integrity. In this work, we ejected intact assemblies from membranes, without chemical disruption, and used mass spectrometry to define their composition. From Escherichia coli outer membranes, we identified a chaperone-porin association and lipid interactions in the β-barrel assembly machinery. We observed efflux pumps bridging inner and outer membranes, and from inner membranes we identified a pentameric pore of TonB, as well as the protein-conducting channel SecYEG in association with F1FO adenosine triphosphate (ATP) synthase. Intact mitochondrial membranes from Bos taurus yielded respiratory complexes and fatty acid-bound dimers of the ADP (adenosine diphosphate)/ATP translocase (ANT-1). These results highlight the importance of native membrane environments for retaining small-molecule binding, subunit interactions, and associated chaperones of the membrane proteome.
Copyright © 2018 The Authors, some rights reserved; exclusive licensee American Association for the Advancement of Science. No claim to original U.S. Government Works.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Comment in
-
A new method to study membrane protein complexes by mass spectrometry.Cardiovasc Res. 2019 Jul 1;115(8):e69-e70. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvz113. Cardiovasc Res. 2019. PMID: 31089690 No abstract available.
-
Comment on "Protein assemblies ejected directly from native membranes yield complexes for mass spectrometry".Science. 2019 Nov 8;366(6466):eaaw9830. doi: 10.1126/science.aaw9830. Epub 2019 Nov 7. Science. 2019. PMID: 31699909
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

