Anti-tumoral potential of MDA19 in human osteosarcoma via suppressing PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway
- PMID: 30442873
- PMCID: PMC6294623
- DOI: 10.1042/BSR20181501
Anti-tumoral potential of MDA19 in human osteosarcoma via suppressing PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway
Abstract
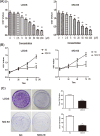
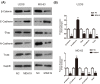
Osteosarcoma (OS) is the most common primary malignancy of skeleton with higher mortality rates amongst children and young adults worldwide, whereas effective and secure therapies have also been sought by researches with ongoing efforts. The purpose of the present study was to investigate the impact of N'-[(3Z)-1-(1-hexyl)-2-oxo-1,2-dihydro-3H-indol-3-ylidene] benzohydrazide (MDA19) on OS and explore its potential mechanism. Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK8) and colony formation assay were employed to evaluate the potential effect of MDA19 on U2OS and MG-63 cells proliferation. Moreover, transwell migration and invasion assay were performed to assess the influence of MDA19 on U2OS and MG-63 cells migration and invasion. In addition, Annexin V-FITC/propidium iodide (Annexin V-FITC/PI) staining and flow cytometry were used to examine apoptotic ratio of the U2OS and MG-63 cells. Meanwhile, Western blot analysis was applied to explore change of relevant mechanism proteins in OS cells treated with MDA19. Our study showed that MDA19 had anti-proliferative activity of OS cells in a dose- and time-dependent manner, simultaneously, inhibition of colony formation was also observed in U2OS and MG-63 cells after incubation of MDA19. Besides, MDA19 could significantly inhibit the number of migrated and invaded OS cells and markedly increase the OS cells apoptosis rate. Mechanistically, we detected detectable reductions in apoptosis related proteins, epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT)-related proteins and activity of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)/Akt/mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) signaling in U2OS and MG-63 cells exposure to MDA19. Overall, the current study indicates in vitro anti-proliferative, anti-metastatic, and pro-apoptotic potential of MDA19 in U2OS and MG-63 cells. Our findings propose a clue for further studies with this compound in preclinical and clinical treatment for OS.
Keywords: EMT; MDA19; Osteosarcoma; PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling.
© 2018 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no competing interests associated with the manuscript.
Figures



References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

