c-Jun N-terminal kinases differentially regulate TNF- and TLRs-mediated necroptosis through their kinase-dependent and -independent activities
- PMID: 30442927
- PMCID: PMC6238001
- DOI: 10.1038/s41419-018-1189-2
c-Jun N-terminal kinases differentially regulate TNF- and TLRs-mediated necroptosis through their kinase-dependent and -independent activities
Abstract
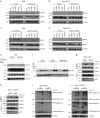
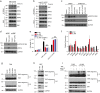
Tumor necrosis factor (TNF) and Toll-like receptor (TLR)3/TLR4 activation trigger necroptotic cell death through downstream signaling complex containing receptor-interacting protein kinase 1 (RIPK1), RIPK3, and pseudokinase mixed lineage kinase-domain-like (MLKL). However, the regulation of necroptotic signaling pathway is far less investigated. Here we showed that c-Jun N-terminal kinases (JNK1 and JNK2) displayed kinase-dependent and -independent functions in regulating TNF- and TLRs-mediated necroptosis. We found that RIPK1 and RIPK3 promoted cell-death-independent JNK activation in macrophages, which contributed to pro-inflammatory cytokines production. Meanwhile, blocking the kinase activity of JNK dramatically reduced TNF and TLRs-induced necroptotic cell death. Consistently, inhibition of JNK activity protected mice from TNF-induced death and Staphylococcus aureus-mediated lung damage. However, depletion of JNK protein using siRNA sensitized macrophages to necroptosis that was triggered by LPS or poly I:C but still inhibited TNF-induced necroptosis. Mechanistic studies revealed that RIPK1 recruited JNK to the necrosome complex and their kinase activity was required for necrosome formation and the phosphorylation of MLKL in TNF- and TLRs-induced necroptosis. Loss of JNK protein consistently suppressed the phosphorylation of MLKL and necrosome formation in TNF-triggered necroptosis, but differentially promoted the phosphorylation of MLKL and necrosome formation in poly I:C-triggered necroptosis by promoting the oligomeration of TRIF. In conclusion, our findings define a differential role for JNK in regulating TNF- and TLRs-mediated necroptosis by their kinase or scaffolding activities.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Protein Kinase-Mediated Decision Between the Life and Death.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2021;1275:1-33. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-49844-3_1. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2021. PMID: 33539010
-
Casein kinase-1γ1 and 3 stimulate tumor necrosis factor-induced necroptosis through RIPK3.Cell Death Dis. 2019 Dec 4;10(12):923. doi: 10.1038/s41419-019-2146-4. Cell Death Dis. 2019. PMID: 31801942 Free PMC article.
-
FKBP12 mediates necroptosis by initiating RIPK1-RIPK3-MLKL signal transduction in response to TNF receptor 1 ligation.J Cell Sci. 2019 May 20;132(10):jcs227777. doi: 10.1242/jcs.227777. J Cell Sci. 2019. PMID: 31028177
-
Necroptosis and Inflammation.Annu Rev Biochem. 2016 Jun 2;85:743-63. doi: 10.1146/annurev-biochem-060815-014830. Epub 2016 Feb 8. Annu Rev Biochem. 2016. PMID: 26865533 Review.
-
Necroptosis in development and diseases.Genes Dev. 2018 Mar 1;32(5-6):327-340. doi: 10.1101/gad.312561.118. Genes Dev. 2018. PMID: 29593066 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A Novel Role for Necroptosis in the Pathogenesis of Necrotizing Enterocolitis.Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020;9(3):403-423. doi: 10.1016/j.jcmgh.2019.11.002. Epub 2019 Nov 19. Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020. PMID: 31756560 Free PMC article.
-
RIP3 in Necroptosis: Underlying Contributions to Traumatic Brain Injury.Neurochem Res. 2024 Feb;49(2):245-257. doi: 10.1007/s11064-023-04038-z. Epub 2023 Sep 25. Neurochem Res. 2024. PMID: 37743445 Review.
-
Toll-Like Receptors as Therapeutic Targets in Central Nervous System Tumors.Biomed Res Int. 2019 May 21;2019:5286358. doi: 10.1155/2019/5286358. eCollection 2019. Biomed Res Int. 2019. PMID: 31240216 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comprehensive analysis of mitochondrial dysfunction and necroptosis in intracranial aneurysms from the perspective of predictive, preventative, and personalized medicine.Apoptosis. 2023 Oct;28(9-10):1452-1468. doi: 10.1007/s10495-023-01865-x. Epub 2023 Jul 6. Apoptosis. 2023. PMID: 37410216 Free PMC article.
-
RIPK3 promoter hypermethylation in hepatocytes protects from bile acid-induced inflammation and necroptosis.Cell Death Dis. 2023 Apr 18;14(4):275. doi: 10.1038/s41419-023-05794-0. Cell Death Dis. 2023. PMID: 37072399 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

