Progressive Feeding Intolerance Secondary to a Congenital Spinal Teratoma in a Four-week-old Female
- PMID: 30443451
- PMCID: PMC6235640
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.3281
Progressive Feeding Intolerance Secondary to a Congenital Spinal Teratoma in a Four-week-old Female
Abstract
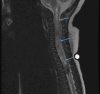
A poorly feeding neonate presents the clinician with a diagnostic challenge. Feeding difficulties and irritability may be due to sepsis, congenital heart disease, inborn errors of metabolism, non-accidental head trauma, as well as a vast variety of other pathologies. Teratomas are rare pediatric tumors that can occasionally present in the immediate neonatal period and can manifest in the infant's central nervous system (CNS) with non-specific symptoms of poor feeding, lethargy, and somnolence. Operative resection remains the cornerstone of treatment; however, there is no well-defined role for adjuvant chemotherapy or radiation in these treatments. We report a case of a four-week-old female presenting with progressive feeding intolerance secondary to a near holocord thoracic spinal teratoma. Her tumor was surgically resected and she was treated with adjuvant chemotherapy and radiation for 13 months and is now in clinical remission. While rare, intramedullary spinal cord lesions should be considered in the differential diagnosis of infants presenting with poor feeding and hypotonia.
Keywords: hospital medicine; neurosurgery; oncology; pediatrics; teaching hospital; teratoma.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

References
-
- Bacterial meningitis and the newborn infant. Pong A, Bradley JS. Infect Dis Clin North Am. 1999;13:711–733. - PubMed
-
- Nizet V, Klein JO. Infectious Diseases of the Fetus and Newborn Infant, 8th ed. Philadelphia: Elsevier Saunders; 2016. Bacterial sepsis and meningitis; pp. 217–271.
-
- Management of infantile colic. Drug and Therapeutics Bulletin. BMJ. 2013;347:0. - PubMed
-
- Intramedullary spinal immature teratoma: resolution of quadriplegia following resection in a 4-week-old infant. Nickols HH, Chambless LB, Carson RP, Coffin CM, Pearson MM, Abel TW. J Neurosurg Pediatrics. 2010;6:586–591. - PubMed
-
- Pediatric intramedullary teratomas. Isik N, Balak N, Silav G, Elmaci I. Neuropediatrics. 2008;39:196–199. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
