Circulating let-7 Levels in Serum Correlate With the Severity of Hepatic Fibrosis in Chronic Hepatitis C
- PMID: 30443558
- PMCID: PMC6231525
- DOI: 10.1093/ofid/ofy268
Circulating let-7 Levels in Serum Correlate With the Severity of Hepatic Fibrosis in Chronic Hepatitis C
Abstract
Background: Evaluating the progression of hepatic fibrosis in chronic hepatitis C (CHC) is critical, and identifying a predictive biomarker for fibrosis will be helpful for implementing personalized surveillance of hepatocellular carcinoma after the elimination of hepatitis C virus by antiviral therapy. This study aimed to investigate the association of circulating let-7a-5p levels with severity of hepatic fibrosis.
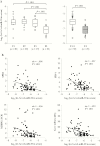
Methods: We analyzed circulating let-7a-5p levels in serum and serum-derived extracellular vesicles (EVs) in 84 Japanese CHC patients who underwent a liver biopsy by quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction, and investigated the association of its levels with histological hepatic fibrotic stage, liver stiffness, and several hepatic fibrotic markers.
Results: The levels of let-7a-5p in serum and EVs were significantly lower in patients with liver cirrhosis. Additionally, the serum let-7a-5p level correlated significantly with hepatic fibrotic markers, Mac-2 binding protein glycan isomer (M2BPGi), fibrosis-4 (FIB-4) index, aspartate aminotransferase-to-platelet ratio index (APRI), and liver stiffness, evaluated by transient elastography. Furthermore, the serum let-7a-5p level was superior to M2BPGi, FIB-4, and APRI and was comparable to liver stiffness in discriminating liver cirrhosis.
Conclusions: These results provide evidence that circulating let-7a-5p in serum may serve as a surrogate marker for severity of hepatic fibrosis in CHC.
Keywords: extracellular vesicles; hepatic fibrosis; hepatitis C virus; let-7; microRNA.
Figures
References
-
- Sterling RK, Lissen E, Clumeck N, et al. APRICOT Clinical Investigators Development of a simple noninvasive index to predict significant fibrosis in patients with HIV/HCV coinfection. Hepatology 2006; 43:1317–25. - PubMed
-
- Wai CT, Greenson JK, Fontana RJ, et al. A simple noninvasive index can predict both significant fibrosis and cirrhosis in patients with chronic hepatitis C. Hepatology 2003; 38:518–26. - PubMed
-
- Kwok R, Tse YK, Wong GL, et al. Systematic review with meta-analysis: non-invasive assessment of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease–the role of transient elastography and plasma cytokeratin-18 fragments. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2014; 39:254–69. - PubMed
-
- Bartel DP. MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell 2004; 116:281–97. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

