Network science approach to modelling the topology and robustness of supply chain networks: a review and perspective
- PMID: 30443587
- PMCID: PMC6214257
- DOI: 10.1007/s41109-017-0053-0
Network science approach to modelling the topology and robustness of supply chain networks: a review and perspective
Abstract
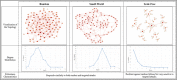
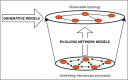
Due to the increasingly complex and interconnected nature of global supply chain networks (SCNs), a recent strand of research has applied network science methods to model SCN growth and subsequently analyse various topological features, such as robustness. This paper provides: (1) a comprehensive review of the methodologies adopted in literature for modelling the topology and robustness of SCNs; (2) a summary of topological features of the real world SCNs, as reported in various data driven studies; and (3) a discussion on the limitations of existing network growth models to realistically represent the observed topological characteristics of SCNs. Finally, a novel perspective is proposed to mimic the SCN topologies reported in empirical studies, through fitness based generative network models.
Keywords: Fitness based attachment; Network science; Supply chain network modelling; Supply network topology and robustness.
Conflict of interest statement
Not applicable.Not applicable.Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Resilience of supply-chain systems under perturbations: A network approach.Chaos. 2022 Sep;32(9):093123. doi: 10.1063/5.0096983. Chaos. 2022. PMID: 36182389
-
Topological motifs populate complex networks through grouped attachment.Sci Rep. 2018 Aug 23;8(1):12670. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-30845-4. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 30140017 Free PMC article.
-
Detecting differences in the topology of scale-free networks grown under time-dynamic topological fitness.Sci Rep. 2020 Jun 30;10(1):10630. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-67156-6. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32606368 Free PMC article.
-
Communication dynamics in complex brain networks.Nat Rev Neurosci. 2017 Dec 14;19(1):17-33. doi: 10.1038/nrn.2017.149. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 29238085 Review.
-
Serous Neoplasms of the Pancreas: A Clinicopathologic Analysis of 193 Cases and Literature Review With New Insights on Macrocystic and Solid Variants and Critical Reappraisal of So-called "Serous Cystadenocarcinoma".Am J Surg Pathol. 2015 Dec;39(12):1597-610. doi: 10.1097/PAS.0000000000000559. Am J Surg Pathol. 2015. PMID: 26559376 Review.
Cited by
-
Assessing the impacts of vaccination and viral evolution in contact networks.Sci Rep. 2024 Jul 8;14(1):15753. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-66070-5. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38977773 Free PMC article.
-
Local topological features of robust supply networks.Appl Netw Sci. 2022;7(1):33. doi: 10.1007/s41109-022-00470-2. Epub 2022 May 20. Appl Netw Sci. 2022. PMID: 35615080 Free PMC article.
-
Testing "efficient supply chain propositions" using topological characterization of the global supply chain network.PLoS One. 2020 Oct 1;15(10):e0239669. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0239669. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 33002029 Free PMC article.
-
Fragility of a multilayer network of intranational supply chains.Appl Netw Sci. 2020;5(1):71. doi: 10.1007/s41109-020-00310-1. Epub 2020 Sep 23. Appl Netw Sci. 2020. PMID: 32984501 Free PMC article.
-
Niche differentiation drives microbial community assembly and succession in full-scale activated sludge bioreactors.NPJ Biofilms Microbiomes. 2022 Apr 11;8(1):23. doi: 10.1038/s41522-022-00291-2. NPJ Biofilms Microbiomes. 2022. PMID: 35411053 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Albert R, Barabási AL. Statistical mechanics of complex networks. Rev Mod Phys. 2002;74(1):47. doi: 10.1103/RevModPhys.74.47. - DOI
-
- Albert R, Jeong H, Barabási AL. Internet: diameter of the world-wide web. Nature. 1999;401(6749):130–131. doi: 10.1038/43601. - DOI
-
- Barabási, A. L. (2014). Network science book. Boston: Center for Complex Network, Northeastern University. Available online at: http://barabasi.com/networksciencebook
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
