Identification of molecular determinants that govern distinct STIM2 activation dynamics
- PMID: 30444880
- PMCID: PMC6267984
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pbio.2006898
Identification of molecular determinants that govern distinct STIM2 activation dynamics
Abstract
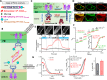
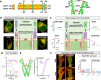
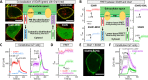
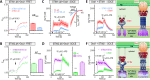
The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) Ca2+ sensors stromal interaction molecule 1 (STIM1) and STIM2, which connect ER Ca2+ depletion with extracellular Ca2+ influx, are crucial for the maintenance of Ca2+ homeostasis in mammalian cells. Despite the recent progress in unraveling the role of STIM2 in Ca2+ signaling, the mechanistic underpinnings of its activation remain underexplored. We use an engineering approach to direct ER-resident STIMs to the plasma membrane (PM) while maintaining their correct membrane topology, as well as Förster resonance energy transfer (FRET) sensors that enabled in cellulo real-time monitoring of STIM activities. This allowed us to determine the calcium affinities of STIM1 and STIM2 both in cellulo and in situ, explaining the current discrepancies in the literature. We also identified the key structural determinants, especially the corresponding G residue in STIM1, which define the distinct activation dynamics of STIM2. The chimeric E470G mutation could switch STIM2 from a slow and weak Orai channel activator into a fast and potent one like STIM1 and vice versa. The systemic dissection of STIM2 activation by protein engineering sets the stage for the elucidation of the regulation and function of STIM2-mediated signaling in mammals.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Cross-talk between N-terminal and C-terminal domains in stromal interaction molecule 2 (STIM2) determines enhanced STIM2 sensitivity.J Biol Chem. 2019 Apr 19;294(16):6318-6332. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA118.006801. Epub 2019 Mar 1. J Biol Chem. 2019. PMID: 30824535 Free PMC article.
-
Interplay between ER Ca2+ Binding Proteins, STIM1 and STIM2, Is Required for Store-Operated Ca2+ Entry.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 May 19;19(5):1522. doi: 10.3390/ijms19051522. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 29783744 Free PMC article.
-
STIM2 Induces Activated Conformation of STIM1 to Control Orai1 Function in ER-PM Junctions.Cell Rep. 2018 Apr 10;23(2):522-534. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2018.03.065. Cell Rep. 2018. PMID: 29642009
-
Molecular physiology and pathophysiology of stromal interaction molecules.Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2018 Mar;243(5):451-472. doi: 10.1177/1535370218754524. Epub 2018 Jan 24. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2018. PMID: 29363328 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Remodelling of the endoplasmic reticulum during store-operated calcium entry.Biol Cell. 2011 Aug;103(8):365-80. doi: 10.1042/BC20100152. Biol Cell. 2011. PMID: 21736554 Review.
Cited by
-
Molecular Mechanism Analysis of STIM1 Thermal Sensation.Cells. 2023 Nov 12;12(22):2613. doi: 10.3390/cells12222613. Cells. 2023. PMID: 37998348 Free PMC article.
-
New insights into the stromal interaction molecule 2 function and its impact on the immunomodulation of tumor microenvironment.Cell Biosci. 2024 Sep 13;14(1):119. doi: 10.1186/s13578-024-01292-8. Cell Biosci. 2024. PMID: 39272139 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of a STIM1 Splicing Variant that Promotes Glioblastoma Growth.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2022 Apr;9(11):e2103940. doi: 10.1002/advs.202103940. Epub 2022 Jan 25. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2022. PMID: 35076181 Free PMC article.
-
Cross-talk between N-terminal and C-terminal domains in stromal interaction molecule 2 (STIM2) determines enhanced STIM2 sensitivity.J Biol Chem. 2019 Apr 19;294(16):6318-6332. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA118.006801. Epub 2019 Mar 1. J Biol Chem. 2019. PMID: 30824535 Free PMC article.
-
Type 3 Inositol 1,4,5-Trisphosphate Receptor is a Crucial Regulator of Calcium Dynamics Mediated by Endoplasmic Reticulum in HEK Cells.Cells. 2020 Jan 22;9(2):275. doi: 10.3390/cells9020275. Cells. 2020. PMID: 31979185 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Prakriya M, Lewis RS. Store-Operated Calcium Channels. Physiol Rev. 2015;95(4):1383–436. Epub 2015/09/25. 10.1152/physrev.00020.2014 ; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC4600950. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Parekh AB, Putney JW Jr. Store-operated calcium channels. Physiol Rev. 2005;85(2):757–810. Epub 2005/03/25. doi: 85/2/757 [pii] 10.1152/physrev.00057.2003 . - DOI - PubMed
-
- Garrity AG, Wang W, Collier CM, Levey SA, Gao Q, Xu H. The endoplasmic reticulum, not the pH gradient, drives calcium refilling of lysosomes. Elife. 2016;5:e15887 Epub 2016/05/24. 10.7554/eLife.15887 ; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC4909396. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Amcheslavsky A, Wood ML, Yeromin AV, Parker I, Freites JA, Tobias DJ, et al. Molecular biophysics of Orai store-operated Ca2+ channels. Biophysical journal. 2015;108(2):237–46. Epub 2015/01/22. 10.1016/j.bpj.2014.11.3473 ; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC4302196. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Soboloff J, Rothberg BS, Madesh M, Gill DL. STIM proteins: dynamic calcium signal transducers. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2012;13(9):549–65. Epub 2012/08/24. 10.1038/nrm3414 [pii]. ; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC3458427. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

