OsTGA2 confers disease resistance to rice against leaf blight by regulating expression levels of disease related genes via interaction with NH1
- PMID: 30444888
- PMCID: PMC6239283
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0206910
OsTGA2 confers disease resistance to rice against leaf blight by regulating expression levels of disease related genes via interaction with NH1
Abstract
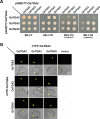
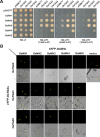
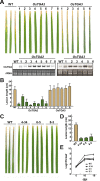
How plants defend themselves from microbial infection is one of the most critical issues for sustainable crop production. Some TGA transcription factors belonging to bZIP superfamily can regulate disease resistance through NPR1-mediated immunity mechanisms in Arabidopsis. Here, we examined biological roles of OsTGA2 (grouped into the same subclade as Arabidopsis TGAs) in bacterial leaf blight resistance. Transcriptional level of OsTGA2 was accumulated after treatment with salicylic acid, methyl jasmonate, and Xathomonas oryzae pv. Oryzae (Xoo), a bacterium causing serious blight of rice. OsTGA2 formed homo- and hetero-dimer with OsTGA3 and OsTGA5 and interacted with rice NPR1 homologs 1 (NH1) in rice. Results of quadruple 9-mer protein-binding microarray analysis indicated that OsTGA2 could bind to TGACGT DNA sequence. Overexpression of OsTGA2 increased resistance of rice to bacterial leaf blight, although overexpression of OsTGA3 resulted in disease symptoms similar to wild type plant upon Xoo infection. Overexpression of OsTGA2 enhanced the expression of defense related genes containing TGA binding cis-element in the promoter such as AP2/EREBP 129, ERD1, and HOP1. These results suggest that OsTGA2 can directly regulate the expression of defense related genes and increase the resistance of rice against bacterial leaf blight disease.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Functional inactivation of OsGCNT induces enhanced disease resistance to Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae in rice.BMC Plant Biol. 2018 Nov 1;18(1):264. doi: 10.1186/s12870-018-1489-9. BMC Plant Biol. 2018. PMID: 30382816 Free PMC article.
-
Functional analysis of rice NPR1-like genes reveals that OsNPR1/NH1 is the rice orthologue conferring disease resistance with enhanced herbivore susceptibility.Plant Biotechnol J. 2007 Mar;5(2):313-24. doi: 10.1111/j.1467-7652.2007.00243.x. Plant Biotechnol J. 2007. PMID: 17309686
-
Overexpression of OsMYC2 Results in the Up-Regulation of Early JA-Rresponsive Genes and Bacterial Blight Resistance in Rice.Plant Cell Physiol. 2016 Sep;57(9):1814-27. doi: 10.1093/pcp/pcw101. Epub 2016 May 19. Plant Cell Physiol. 2016. PMID: 27335352
-
Rice Routes of Countering Xanthomonas oryzae.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Oct 2;19(10):3008. doi: 10.3390/ijms19103008. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30279356 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Development of disease-resistant rice using regulatory components of induced disease resistance.Front Plant Sci. 2014 Nov 13;5:630. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2014.00630. eCollection 2014. Front Plant Sci. 2014. PMID: 25431577 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A mini-TGA protein modulates gene expression through heterogeneous association with transcription factors.Plant Physiol. 2023 Mar 17;191(3):1934-1952. doi: 10.1093/plphys/kiac579. Plant Physiol. 2023. PMID: 36517238 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphorylation of OsTGA5 by casein kinase II compromises its suppression of defense-related gene transcription in rice.Plant Cell. 2022 Aug 25;34(9):3425-3442. doi: 10.1093/plcell/koac164. Plant Cell. 2022. PMID: 35642941 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptome analysis reveals differential transcription in tomato (Solanum lycopersicum) following inoculation with Ralstonia solanacearum.Sci Rep. 2022 Dec 22;12(1):22137. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-26693-y. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 36550145 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-Wide Identification and Expression Analysis of the TGA Gene Family in Banana (Musa nana Lour.) Under Various Nitrogen Conditions.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Feb 28;26(5):2168. doi: 10.3390/ijms26052168. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40076789 Free PMC article.
-
OsbZIP81, A Homologue of Arabidopsis VIP1, May Positively Regulate JA Levels by Directly Targetting the Genes in JA Signaling and Metabolism Pathway in Rice.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 May 13;20(9):2360. doi: 10.3390/ijms20092360. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31086007 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bigeard J, Colcombet J, Hirt H. Signaling Mechanisms in Pattern-Triggered Immunity (PTI). Cell Signal. 2015;8: 521–539. 10.1016/j.molp.2014.12.022 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Kumar D. Salicylic acid signaling in disease resistance. Plant Sci. 2014;228: 127–134. 10.1016/j.plantsci.2014.04.014 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Delaney TP, Uknes S, Vernooij B, Friedrich L, Weymann K, Negrotto D, et al. A central role of salicylic acid in plant disease resistance. Science. 1994;266: 1247 10.1126/science.266.5188.1247 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Vernooij B, Friedrich L, Morse A, Reist R, Kolditz-Jawhar R, Ward E, et al. Salicylic acid is not the translocated signal responsible for inducing systemic acquired resistance but is required in signal transduction. Plant Cell. 1994;6: 959 10.1105/tpc.6.7.959 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bai W, Chern M, Ruan D, Canlas PE, Sze-to WH, Ronald PC. Enhanced disease resistance and hypersensitivity to BTH by introduction of an NH1/OsNPR1 paralog. Plant Biotechnol J. 2011;9: 205–215. 10.1111/j.1467-7652.2010.00544.x - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

