Clinical outcomes of hypofractionated image-guided multifocal irradiation using volumetric-modulated arc therapy for brain metastases
- PMID: 30445426
- PMCID: PMC6373671
- DOI: 10.1093/jrr/rry091
Clinical outcomes of hypofractionated image-guided multifocal irradiation using volumetric-modulated arc therapy for brain metastases
Abstract
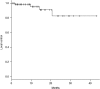
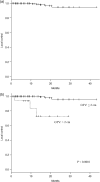
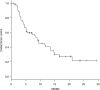
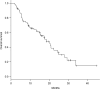
Volumetric-modulated arc therapy (VMAT) can be used to design hypofractionated radiotherapy treatment plans for multiple brain metastases. The purpose of this study was to evaluate treatment outcomes of hypofractionated image-guided multifocal irradiation using VMAT (HFIGMI-VMAT) for brain metastases. From July 2012 to December 2016, 67 consecutive patients with 601 brain metastases were treated with HFIGMI-VMAT at our institution. The prescribed dose was 50 Gy to a 95% volume of the planning target volume in 10 fractions. Fifty-five of the 67 patients had non-small-cell lung cancer, and the remaining 12 had other types of cancer. The median number of brain metastases was five, and the median maximum diameter was 1.2 cm. The median duration of follow-up was 12.0 months (range, 1.9-44.8 months), and the median survival time 18.7 months. Four patients with six lesions had local recurrences. The local control rate in the 64 assessed patients was 98.4% and 95.3% at 6 and 12 months, respectively (three died before assessment). The local control rate for the 572 assessed lesions was 99.8% and 99.3% at 6 and 12 months, respectively. Thirty-nine patients developed distant brain metastases, the distant brain control rate being 59.7% and 40.5% at 6 and 12 months, respectively. Acute toxicities were generally mild (Grade 1-2). Three patients (4.5%) developed radiation necrosis requiring corticosteroid therapy. The HFIGMI-VMAT technique with flat dose delivery was well tolerated and achieved excellent local control. This technique is a promising treatment option for patients with multiple and large brain metastases.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effective method to reduce the normal brain dose in single-isocenter hypofractionated stereotactic radiotherapy for multiple brain metastases.Strahlenther Onkol. 2021 Jul;197(7):592-600. doi: 10.1007/s00066-021-01757-6. Epub 2021 Mar 16. Strahlenther Onkol. 2021. PMID: 33725135
-
Moderate Hypofractionated Postprostatectomy Volumetric Modulated Arc Therapy With Daily Image Guidance (VMAT-IGRT): A Mono-institutional Report on Feasibility and Acute Toxicity.Clin Genitourin Cancer. 2017 Aug;15(4):e667-e673. doi: 10.1016/j.clgc.2017.01.025. Epub 2017 Feb 6. Clin Genitourin Cancer. 2017. PMID: 28237181
-
Dosimetric characterization of hypofractionated Gamma Knife radiosurgery of large or complex brain tumors versus linear accelerator-based treatments.J Neurosurg. 2016 Dec;125(Suppl 1):97-103. doi: 10.3171/2016.7.GKS16881. J Neurosurg. 2016. PMID: 27903198
-
Dosimetric comparison between dual-isocentric dynamic conformal arc therapy and mono-isocentric volumetric-modulated arc therapy for two large brain metastases.J Radiat Res. 2018 Nov 1;59(6):774-781. doi: 10.1093/jrr/rry064. J Radiat Res. 2018. PMID: 30102325 Free PMC article.
-
Treatment of brain oligometastases with hypofractionated stereotactic radiotherapy utilising volumetric modulated arc therapy.Clin Exp Metastasis. 2016 Feb;33(2):125-32. doi: 10.1007/s10585-015-9762-x. Epub 2015 Oct 19. Clin Exp Metastasis. 2016. PMID: 26482476
Cited by
-
Analysis of prostate intensity- and volumetric-modulated arc radiation therapy planning quality with PlanIQTM.J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2021 Apr;22(4):132-142. doi: 10.1002/acm2.13233. Epub 2021 Mar 25. J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2021. PMID: 33768648 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative evaluation of two dose-volume histogram prediction tools for treatment planning: Treatment planning quality and dose verification accuracy.Tech Innov Patient Support Radiat Oncol. 2024 Dec 13;33:100297. doi: 10.1016/j.tipsro.2024.100297. eCollection 2025 Mar. Tech Innov Patient Support Radiat Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39807442 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Soffietti R, Ruda R, Mutani R. Management of brain metastases. J Neurol 2002;249:1357–69. - PubMed
-
- Tabouret E, Chinot O, Metellus P et al. . Recent trends in epidemiology of brain metastases: an overview. Anticancer Res 2012;32:4655–62. - PubMed
-
- Nayak L, Lee EQ, Wen PY. Epidemiology of brain metastases. Curr Oncol Rep 2011;14:48–54. - PubMed
-
- Nieder C, Spanne O, Mehta MP et al. . Presentation, patterns of care, and survival in patients with brain metastases. Cancer 2011;117:2505–12. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical