KrakenUniq: confident and fast metagenomics classification using unique k-mer counts
- PMID: 30445993
- PMCID: PMC6238331
- DOI: 10.1186/s13059-018-1568-0
KrakenUniq: confident and fast metagenomics classification using unique k-mer counts
Abstract
False-positive identifications are a significant problem in metagenomics classification. We present KrakenUniq, a novel metagenomics classifier that combines the fast k-mer-based classification of Kraken with an efficient algorithm for assessing the coverage of unique k-mers found in each species in a dataset. On various test datasets, KrakenUniq gives better recall and precision than other methods and effectively classifies and distinguishes pathogens with low abundance from false positives in infectious disease samples. By using the probabilistic cardinality estimator HyperLogLog, KrakenUniq runs as fast as Kraken and requires little additional memory. KrakenUniq is freely available at https://github.com/fbreitwieser/krakenuniq .
Keywords: Infectious disease diagnosis; Metagenomics; Metagenomics classification; Microbiome; Pathogen detection.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures

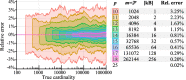

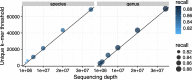
References
-
- Thoendel M, Jeraldo P, Greenwood-Quaintance KE, Yao J, Chia N, Hanssen AD, Abdel MP, Patel R. Impact of contaminating DNA in whole-genome amplification kits used for metagenomic shotgun sequencing for infection diagnosis. J Clin Microbiol. 2017;55:1789–1801. doi: 10.1128/JCM.02402-16. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Salzberg SL, Breitwieser FP, Kumar A, Hao H, Burger P, Rodriguez FJ, Lim M, Quinones-Hinojosa A, Gallia GL, Tornheim JA, et al. Next-generation sequencing in neuropathologic diagnosis of infections of the nervous system. Neurol Neuroimmunol Neuroinflamm. 2016;3:e251. doi: 10.1212/NXI.0000000000000251. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

