Modulators of inflammation in Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia
- PMID: 30446300
- PMCID: PMC6368974
- DOI: 10.1053/j.semperi.2018.09.009
Modulators of inflammation in Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia
Abstract
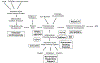
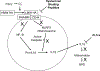
Over 50 years after its first description, Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia (BPD) remains a devastating pulmonary complication in preterm infants with respiratory failure and develops in 30-50% of infants less than 1000-gram birth weight. It is thought to involve ventilator- and oxygen-induced damage to an immature lung that results in an inflammatory response and ends in aberrant lung development with dysregulated angiogenesis and alveolarization. Significant morbidity and mortality are associated with this most common chronic lung disease of childhood. Thus, any therapies that decrease the incidence or severity of this condition would have significant impact on morbidity, mortality, human costs, and healthcare expenditure. It is clear that an inflammatory response and the elaboration of growth factors and cytokines are associated with the development of BPD. Numerous approaches to control the inflammatory process leading to the development of BPD have been attempted. This review will examine the anti-inflammatory approaches that are established or hold promise for the prevention or treatment of BPD.
Copyright © 2018. Published by Elsevier Inc.
Figures
References
-
- Ambalavanan N, Carlo WA. Bronchopulmonary dysplasia: new insights. Clin Perinatol 2004;31(3):613–628. - PubMed
-
- Bhandari A, Bhandari V. Pathogenesis, pathology and pathophysiology of pulmonary sequelae of bronchopulmonary dysplasia in premature infants. Front Biosci 2003;8:e370–380. - PubMed
-
- Speer CP. Inflammation and bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Semin Neonatol 2003;8(1):29–38. - PubMed
-
- Rindfleisch MS, Hasday JD, Taciak V, Boderick K, Viscardi RM. Potential role of interleukin-1 in the development of bronchopulmonary dysplasia. J Interferon Cytokine Res 1996;16:365–373. - PubMed
-
- Stenmark KR, Abman SH. Lung vascular development: implications for the pathogenesis of bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Annu Rev Physiol 2005;67:623–661. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

