Glial Sulfatides and Neuronal Complex Gangliosides Are Functionally Interdependent in Maintaining Myelinating Axon Integrity
- PMID: 30446529
- PMCID: PMC6325269
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2095-18.2018
Glial Sulfatides and Neuronal Complex Gangliosides Are Functionally Interdependent in Maintaining Myelinating Axon Integrity
Abstract
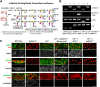
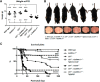
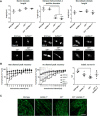
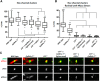
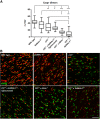
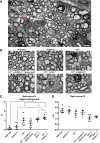
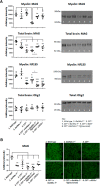
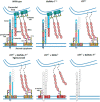
Sulfatides and gangliosides are raft-associated glycolipids essential for maintaining myelinated nerve integrity. Mice deficient in sulfatide (cerebroside sulfotransferase knock-out, CST-/-) or complex gangliosides (β-1,4-N-acetylegalactosaminyltransferase1 knock-out, GalNAc-T-/-) display prominent disorganization of proteins at the node of Ranvier (NoR) in early life and age-dependent neurodegeneration. Loss of neuronal rather than glial complex gangliosides underpins the GalNAc-T-/- phenotype, as shown by neuron- or glial-specific rescue, whereas sulfatide is principally expressed and functional in glial membranes. The similarities in NoR phenotype of CST-/-, GalNAc-T-/-, and axo-glial protein-deficient mice suggests that these glycolipids stabilize membrane proteins including neurofascin155 (NF155) and myelin-associated glycoprotein (MAG) at axo-glial junctions. To assess the functional interactions between sulfatide and gangliosides, CST-/- and GalNAc-T-/- genotypes were interbred. CST-/-× GalNAc-T-/- mice develop normally to postnatal day 10 (P10), but all die between P20 and P25, coinciding with peak myelination. Ultrastructural, immunohistological, and biochemical analysis of either sex revealed widespread axonal degeneration and disruption to the axo-glial junction at the NoR. In addition to sulfatide-dependent loss of NF155, CST-/- × GalNAc-T-/- mice exhibited a major reduction in MAG protein levels in CNS myelin compared with WT and single-lipid-deficient mice. The CST-/- × GalNAc-T-/- phenotype was fully restored to that of CST-/- mice by neuron-specific expression of complex gangliosides, but not by their glial-specific expression nor by the global expression of a-series gangliosides. These data indicate that sulfatide and complex b-series gangliosides on the glial and neuronal membranes, respectively, act in concert to promote NF155 and MAG in maintaining the stable axo-glial interactions essential for normal nerve function.SIGNIFICANCE STATEMENT Sulfatides and complex gangliosides are membrane glycolipids with important roles in maintaining nervous system integrity. Node of Ranvier maintenance in particular requires stable compartmentalization of multiple membrane proteins. The axo-glial adhesion molecules neurofascin155 (NF155) and myelin-associated glycoprotein (MAG) require membrane microdomains containing either sulfatides or complex gangliosides to localize and function effectively. The cooperative roles of these microdomains and associated proteins are unknown. Here, we show vital interdependent roles for sulfatides and complex gangliosides because double (but not single) deficiency causes a rapidly lethal phenotype at an early age. These findings suggest that sulfatides and complex gangliosides on opposing axo-glial membranes are responsible for essential tethering of the axo-glial junction proteins NF155 and MAG, which interact to maintain the nodal complex.
Keywords: MAG; NF155; axo–glial integrity; ganglioside; node of Ranvier; sulfatide.
Copyright © 2019 McGonigal et al.
Figures
Comment in
-
Importance of Lipids for Nervous System Integrity: Cooperation between Gangliosides and Sulfatides in Myelin Stability.J Neurosci. 2019 Aug 7;39(32):6218-6220. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0377-19.2019. J Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 31391258 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Neuronally expressed a-series gangliosides are sufficient to prevent the lethal age-dependent phenotype in GM3-only expressing mice.J Neurochem. 2021 Jul;158(2):217-232. doi: 10.1111/jnc.15365. Epub 2021 May 12. J Neurochem. 2021. PMID: 33864399
-
An oligodendrocyte cell adhesion molecule at the site of assembly of the paranodal axo-glial junction.J Cell Biol. 2000 Aug 7;150(3):657-66. doi: 10.1083/jcb.150.3.657. J Cell Biol. 2000. PMID: 10931875 Free PMC article.
-
In vitro analysis of glial cell function in ganglioside-deficient mice.J Neurosci Res. 2009 Aug 15;87(11):2467-83. doi: 10.1002/jnr.22085. J Neurosci Res. 2009. PMID: 19382235
-
The Role of Sulfatides in Axon-Glia Interactions.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2019;1190:165-179. doi: 10.1007/978-981-32-9636-7_11. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2019. PMID: 31760644 Review.
-
Galactolipids are molecular determinants of myelin development and axo-glial organization.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2002 Dec 19;1573(3):406-13. doi: 10.1016/s0304-4165(02)00410-5. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2002. PMID: 12417425 Review.
Cited by
-
Ganglioside lipidomics of CNS myelination using direct infusion shotgun mass spectrometry.iScience. 2022 Oct 10;25(11):105323. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2022.105323. eCollection 2022 Nov 18. iScience. 2022. PMID: 36310581 Free PMC article.
-
Functional Impairment of the Nervous System with Glycolipid Deficiencies.Adv Neurobiol. 2023;29:419-448. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-12390-0_14. Adv Neurobiol. 2023. PMID: 36255683 Free PMC article.
-
The role of gangliosides in the organisation of the node of Ranvier examined in glycosyltransferase transgenic mice.J Anat. 2022 Nov;241(5):1259-1271. doi: 10.1111/joa.13562. Epub 2021 Oct 3. J Anat. 2022. PMID: 34605014 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Multiple Roles of Apolipoprotein E4 in Oxidative Lipid Metabolism and Ferroptosis During the Pathogenesis of Alzheimer's Disease.J Mol Neurosci. 2024 Jul 3;74(3):62. doi: 10.1007/s12031-024-02224-4. J Mol Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 38958788 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Altered plasma membrane abundance of the sulfatide-binding protein NF155 links glycosphingolipid imbalances to demyelination.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2023 Apr 4;120(14):e2218823120. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2218823120. Epub 2023 Mar 30. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2023. PMID: 36996106 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bhat MA, Rios JC, Lu Y, Garcia-Fresco GP, Ching W, St Martin M, Li J, Einheber S, Chesler M, Rosenbluth J, Salzer JL, Bellen HJ (2001) Axon-glia interactions and the domain organization of myelinated axons requires neurexin IV/Caspr/Paranodin. Neuron 30:369–383. 10.1016/S0896-6273(01)00294-X - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bowes T, Wagner ER, Boffey J, Nicholl D, Cochrane L, Benboubetra M, Conner J, Furukawa K, Furukawa K, Willison HJ (2002) Tolerance to self-gangliosides is the major factor restricting the antibody response to lipopolysaccharide core oligosaccharides in campylobacter jejuni strains associated with guillain-barre syndrome. Infect Immun 70:5008–5018. 10.1128/IAI.70.9.5008-5018.2002 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
