Induction of MNK Kinase-dependent eIF4E Phosphorylation by Inhibitors Targeting BET Proteins Limits Efficacy of BET Inhibitors
- PMID: 30446586
- PMCID: PMC6363873
- DOI: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-18-0768
Induction of MNK Kinase-dependent eIF4E Phosphorylation by Inhibitors Targeting BET Proteins Limits Efficacy of BET Inhibitors
Abstract
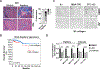
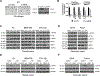
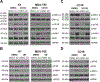
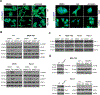
BET inhibitors (BETi), which target transcription of key oncogenic genes, are currently being evaluated in early-phase clinical trials. However, because BETis show limited single-agent activity, there is increasing interest in identifying signaling pathways to enhance the efficacy of BETis. Here, we demonstrate increased MNK kinase-dependent eIF4E phosphorylation following treatment with BETis, indicating activation of a prosurvival feedback mechanism in response to BETis. BET PROTACs, which promote degradation of BET proteins, also induced eIF4E phosphorylation in cancer cells. Mechanistically, we show that the effect of BETis on MNK-eIF4E phosphorylation was mediated by p38 MAPKs. We also show that BETis suppressed RacGAP1 to induce Rac signaling-mediated eIF4E phosphorylation. Significantly, MNK inhibitors and MNK1/2 knockdown enhanced the efficacy of BETis in suppressing proliferation of cancer cells in vitro and in a syngeneic mouse model. Together, these results demonstrate a novel prosurvival feedback signaling induced by BETis, providing a mechanistic rationale for combination therapy with BET and MNK inhibitors for synergistic inhibition of cancer cells.
©2018 American Association for Cancer Research.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure of Potential Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no potential conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
CGP57380 enhances efficacy of RAD001 in non-small cell lung cancer through abrogating mTOR inhibition-induced phosphorylation of eIF4E and activating mitochondrial apoptotic pathway.Oncotarget. 2016 May 10;7(19):27787-801. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.8497. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27050281 Free PMC article.
-
The androgen receptor is a negative regulator of eIF4E phosphorylation at S209: implications for the use of mTOR inhibitors in advanced prostate cancer.Oncogene. 2017 Nov 16;36(46):6359-6373. doi: 10.1038/onc.2017.233. Epub 2017 Jul 24. Oncogene. 2017. PMID: 28745319 Free PMC article.
-
Synergistic efficacy of inhibiting MYCN and mTOR signaling against neuroblastoma.BMC Cancer. 2021 Sep 26;21(1):1061. doi: 10.1186/s12885-021-08782-9. BMC Cancer. 2021. PMID: 34565342 Free PMC article.
-
Progress in developing MNK inhibitors.Eur J Med Chem. 2021 Jul 5;219:113420. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2021.113420. Epub 2021 Apr 2. Eur J Med Chem. 2021. PMID: 33892273 Review.
-
Targeting Mnks for cancer therapy.Oncotarget. 2012 Feb;3(2):118-31. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.453. Oncotarget. 2012. PMID: 22392765 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Biological functions and research progress of eIF4E.Front Oncol. 2023 Aug 3;13:1076855. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1076855. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37601696 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Phosphorylation of the mRNA cap-binding protein eIF4E and cancer.Cell Signal. 2020 Sep;73:109689. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2020.109689. Epub 2020 Jun 11. Cell Signal. 2020. PMID: 32535199 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fixing the GAP: The role of RhoGAPs in cancer.Eur J Cell Biol. 2022 Apr;101(2):151209. doi: 10.1016/j.ejcb.2022.151209. Epub 2022 Feb 10. Eur J Cell Biol. 2022. PMID: 35180567 Free PMC article. Review.
-
XP-524 is a dual-BET/EP300 inhibitor that represses oncogenic KRAS and potentiates immune checkpoint inhibition in pancreatic cancer.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2022 Jan 25;119(4):e2116764119. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2116764119. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2022. PMID: 35064087 Free PMC article.
-
The role of eIF4F-driven mRNA translation in regulating the tumour microenvironment.Nat Rev Cancer. 2023 Jun;23(6):408-425. doi: 10.1038/s41568-023-00567-5. Epub 2023 May 4. Nat Rev Cancer. 2023. PMID: 37142795 Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

