Overexpression of the CORVET complex alleviates the fungicidal effects of fludioxonil on the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae expressing hybrid histidine kinase 3
- PMID: 30446623
- PMCID: PMC6333885
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.RA118.004736
Overexpression of the CORVET complex alleviates the fungicidal effects of fludioxonil on the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae expressing hybrid histidine kinase 3
Abstract
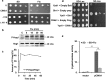
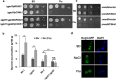
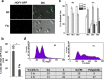
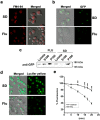
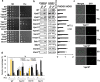
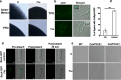
The hybrid histidine kinase 3 (HHK3) is a highly conserved sensor kinase in fungi that regulates the downstream HOG/p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK). In addition to its role in osmoadaptation, HHK3 is involved in hyphal morphogenesis, conidiation, virulence, and cellular adaptation to oxidative stress. However, the molecular mechanisms by which it controls these processes remain obscure. Moreover, HHK3 is a molecular target for antifungal agents such as fludioxonil, which thereby interferes with the HOG/p38 pathway, leading to the abnormal accumulation of glycerol and subsequent cell lysis. Here, we used a chemical genomics approach with the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae to better understand the fungicidal action of fludioxonil and the role of HHK3 in fungal growth and physiology. Our results indicated that the abnormal accumulation of glycerol is not the primary cause of fludioxonil toxicity. Fludioxonil appears to impair endosomal trafficking in the fungal cells. We found that the components of class C core vacuole/endosome tethering (CORVET) complex are essential for yeast viability in the presence of a subthreshold dose of fludioxonil and that their overexpression alleviates fludioxonil toxicity. We also noted that by impeding secretory vesicle trafficking, fludioxonil inhibits hyphal growth in the opportunistic fungal pathogen Candida albicans Our results suggest that HHK3 regulates fungal hyphal growth by affecting vesicle trafficking. Together, our results reveal an important role of CORVET complex in the fungicidal action of fludioxonil downstream of HHK3.
Keywords: Candida albicans; HOG/p38 pathway; MAPK signaling; antifungal agent; cell signaling; filamentous growth; fludioxonil; fungi; histidine kinase; hybrid histidine kinase 3; mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK); p38 MAPK; vesicle trafficking; yeast.
© 2019 Randhawa et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest with the contents of this article
Figures
Similar articles
-
Distinct role of HAMP and HAMP-like linker domains in regulating the activity of Hik1p, a hybrid histidine kinase 3 from Magnaporthe oryzae.Mol Genet Genomics. 2021 Sep;296(5):1135-1145. doi: 10.1007/s00438-021-01809-7. Epub 2021 Jul 1. Mol Genet Genomics. 2021. PMID: 34196769
-
Overexpression of CBK1 or deletion of SSD1 confers fludioxonil resistance in yeast by suppressing Hog1 activation.Gene. 2025 Jan 15;933:148905. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2024.148905. Epub 2024 Aug 30. Gene. 2025. PMID: 39218413
-
Fludioxonil Induces Drk1, a Fungal Group III Hybrid Histidine Kinase, To Dephosphorylate Its Downstream Target, Ypd1.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2017 Jan 24;61(2):e01414-16. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01414-16. Print 2017 Feb. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2017. PMID: 27872062 Free PMC article.
-
Yeast go the whole HOG for the hyperosmotic response.Trends Genet. 2002 Aug;18(8):405-12. doi: 10.1016/s0168-9525(02)02723-3. Trends Genet. 2002. PMID: 12142009 Review.
-
The HOG pathway and the regulation of osmoadaptive responses in yeast.FEMS Yeast Res. 2022 Mar 25;22(1):foac013. doi: 10.1093/femsyr/foac013. FEMS Yeast Res. 2022. PMID: 35254447 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
BEM2, a RHO GTPase Activating Protein That Regulates Morphogenesis in S. cerevisiae, Is a Downstream Effector of Fungicidal Action of Fludioxonil.J Fungi (Basel). 2022 Jul 21;8(7):754. doi: 10.3390/jof8070754. J Fungi (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35887509 Free PMC article.
-
Distinct role of HAMP and HAMP-like linker domains in regulating the activity of Hik1p, a hybrid histidine kinase 3 from Magnaporthe oryzae.Mol Genet Genomics. 2021 Sep;296(5):1135-1145. doi: 10.1007/s00438-021-01809-7. Epub 2021 Jul 1. Mol Genet Genomics. 2021. PMID: 34196769
-
Convergent and distinctive functions of transcription factors VdYap1, VdAtf1, and VdSkn7 in the regulation of nitrosative stress resistance, microsclerotia formation, and virulence in Verticillium dahliae.Mol Plant Pathol. 2020 Nov;21(11):1451-1466. doi: 10.1111/mpp.12988. Epub 2020 Sep 20. Mol Plant Pathol. 2020. PMID: 32954659 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptome Variations in Verticillium dahliae in Response to Two Different Inorganic Nitrogen Sources.Front Microbiol. 2021 Jul 28;12:712701. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.712701. eCollection 2021. Front Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 34394062 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Scorzoni L., de Paula E. Silva A. C., Marcos C. M., Assato P. A., de Melo W. C., de Oliveira H. C., Costa-Orlandi C. B., Mendes-Giannini M. J., and Fusco-Almeida A. M. (2017) Antifungal therapy: new advances in the understanding and treatment of mycosis. Front. Microbiol. 8, 36 10.3389/fmicb.2017.00036 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Corran A., Knauf-Beiter G., and Zeun R. (2008) Fungicides acting on signal transduction, in Modern Crop Protection Compounds (Krämer W., and Schirmer U., eds) pp. 561–580, Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH, Weinheim, Germany
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

