CYP6AE gene cluster knockout in Helicoverpa armigera reveals role in detoxification of phytochemicals and insecticides
- PMID: 30446639
- PMCID: PMC6240031
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-018-07226-6
CYP6AE gene cluster knockout in Helicoverpa armigera reveals role in detoxification of phytochemicals and insecticides
Abstract
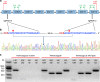
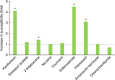
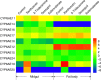
The cotton bollworm Helicoverpa armigera, is one of the world's major pest of agriculture, feeding on over 300 hosts in 68 plant families. Resistance cases to most insecticide classes have been reported for this insect. Management of this pest in agroecosystems relies on a better understanding of how it copes with phytochemical or synthetic toxins. We have used genome editing to knock out a cluster of nine P450 genes and show that this significantly reduces the survival rate of the insect when exposed to two classes of host plant chemicals and two classes of insecticides. Functional expression of all members of this gene cluster identified the P450 enzymes capable of metabolism of these xenobiotics. The CRISPR-Cas9-based reverse genetics approach in conjunction with in vitro metabolism can rapidly identify the contributions of insect P450s in xenobiotic detoxification and serve to identify candidate genes for insecticide resistance.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Heckel DG. Insect detoxification and sequestration strategies. Annu. Plant Rev. 2014;47:77–144. doi: 10.1002/9781118829783.ch3. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

