Immunomodulatory activity of lenvatinib contributes to antitumor activity in the Hepa1-6 hepatocellular carcinoma model
- PMID: 30447042
- PMCID: PMC6272102
- DOI: 10.1111/cas.13806
Immunomodulatory activity of lenvatinib contributes to antitumor activity in the Hepa1-6 hepatocellular carcinoma model
Abstract
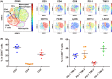
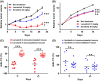
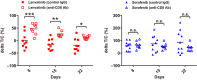
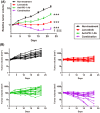
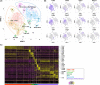
Angiogenesis inhibitors such as lenvatinib and sorafenib, and an immune checkpoint inhibitor (ICI), nivolumab, are used for anticancer therapies against advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Combination treatments comprising angiogenesis inhibitors plus ICIs are promising options for improving clinical benefits in HCC patients, and clinical trials are ongoing. Here, we investigated the antitumor and immunomodulatory activities of lenvatinib (a multiple receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor targeting vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 1-3, fibroblast growth factor receptor 1-4, platelet-derived growth factor receptor α, KIT and RET) and the combined antitumor activity of lenvatinib plus anti-programmed cell death 1 (PD-1) antibody in the Hepa1-6 mouse HCC syngeneic model. We found that the antitumor activities of lenvatinib and sorafenib were not different in immunodeficient mice, but lenvatinib showed more potent antitumor activity than sorafenib in immunocompetent mice. The antitumor activity of lenvatinib was greater in immunocompetent mice than in immunodeficient mice and was attenuated by CD8+ T cell depletion. Treatment with lenvatinib plus anti-PD-1 antibody resulted in more tumor regression and a higher response rate compared with either treatment alone in immunocompetent mice. Single-cell RNA sequencing analysis demonstrated that treatment with lenvatinib with or without anti-PD-1 antibody decreased the proportion of monocytes and macrophages population and increased that of CD8+ T cell populations. These data suggest that lenvatinib has immunomodulatory activity that contributes to the antitumor activity of lenvatinib and enhances the antitumor activity in combination treatment with anti-PD-1 antibody. Combination treatment of lenvatinib plus anti-PD-1 antibody therefore warrants further investigation against advanced HCC.
Keywords: anti-PD-1 antibody; hepatocellular carcinoma; immunomodulatory activity; lenvatinib; sorafenib.
© 2018 The Authors. Cancer Science published by John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd on behalf of Japanese Cancer Association.
Figures
References
-
- Llovet JM, Zucman‐Rossi J, Pikarsky E, et al. Hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2016;2:16018. - PubMed
-
- Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J, Lortet‐Tieulent J, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin. 2015;65:87‐108. - PubMed
-
- Llovet JM, Ricci S, Mazzaferro V, et al. Sorafenib in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2008;359:378‐390. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

