Analysis of post-transcriptional RNA metabolism in prokaryotes
- PMID: 30448478
- PMCID: PMC6568318
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ymeth.2018.11.006
Analysis of post-transcriptional RNA metabolism in prokaryotes
Abstract
Post-transcriptional RNA metabolic pathways play important roles in permitting prokaryotes to operate under a variety of environmental conditions. Although significant progress has been made during the last decade in deciphering RNA processing pathways in a number of bacteria, a complete understanding of post-transcriptional RNA metabolism in any single microorganism is far from reality. Here we describe multiple experimental approaches that can be used to study mRNA stability, tRNA and rRNA processing, sRNA metabolism, and polyadenylation in prokaryotes. The methods described here can be readily utilized in both Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacteria with simple modifications.
Keywords: Cleavage specificity; Northern analysis; RNA isolation; RNAseq; SMART cDNA; mRNA decay; tRNA processing.
Copyright © 2018 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
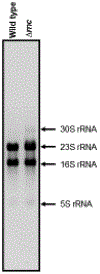
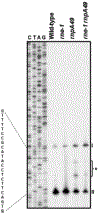
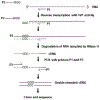

Similar articles
-
Inactivation of RNase P in Escherichia coli significantly changes post-transcriptional RNA metabolism.Mol Microbiol. 2022 Jan;117(1):121-142. doi: 10.1111/mmi.14808. Epub 2021 Sep 25. Mol Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 34486768 Free PMC article.
-
Biosynthesis and function of posttranscriptional modifications of transfer RNAs.Annu Rev Genet. 2012;46:69-95. doi: 10.1146/annurev-genet-110711-155641. Epub 2012 Aug 16. Annu Rev Genet. 2012. PMID: 22905870 Review.
-
Nucleolytic processing of ribonucleic acid transcripts in procaryotes.Microbiol Rev. 1986 Dec;50(4):428-51. doi: 10.1128/mr.50.4.428-451.1986. Microbiol Rev. 1986. PMID: 2432388 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
-
Absolute Regulatory Small Noncoding RNA Concentration and Decay Rates Measurements in Escherichia coli.Methods Mol Biol. 2018;1737:231-248. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-7634-8_14. Methods Mol Biol. 2018. PMID: 29484597
-
Direct RNA sequencing of the Escherichia coli epitranscriptome uncovers alterations under heat stress.Nucleic Acids Res. 2025 Mar 20;53(6):gkaf175. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkaf175. Nucleic Acids Res. 2025. PMID: 40114376 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
mRNA Metabolism in Cardiac Development and Disease: Life After Transcription.Physiol Rev. 2020 Apr 1;100(2):673-694. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00007.2019. Epub 2019 Nov 21. Physiol Rev. 2020. PMID: 31751167 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Generation of pre-tRNAs from polycistronic operons is the essential function of RNase P in Escherichia coli.Nucleic Acids Res. 2020 Mar 18;48(5):2564-2578. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkz1188. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020. PMID: 31993626 Free PMC article.
-
The C nucleotide at the mature 5' end of the Escherichia coli proline tRNAs is required for the RNase E cleavage specificity at the 3' terminus as well as functionality.Nucleic Acids Res. 2022 Feb 22;50(3):1639-1649. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkab1260. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022. PMID: 35061897 Free PMC article.
-
Inactivation of RNase P in Escherichia coli significantly changes post-transcriptional RNA metabolism.Mol Microbiol. 2022 Jan;117(1):121-142. doi: 10.1111/mmi.14808. Epub 2021 Sep 25. Mol Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 34486768 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mohanty BK, and Kushner SR, Analysis of the function of Escherichia coli poly(A) polymerase I in RNA metabolism, Mol Microbiol 34 (1999) 1094–108. - PubMed
-
- Hambraeus G, von Wachenfeldt C, and Hederstedt L, Genome-wide survey of mRNA half-lives in Bacillus subtilis identifies extremely stable mRNAs, Mol Genet Genomics 269 (2003) 706–14. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

