Carnosine protects cardiac myocytes against lipid peroxidation products
- PMID: 30449006
- PMCID: PMC6377314
- DOI: 10.1007/s00726-018-2676-6
Carnosine protects cardiac myocytes against lipid peroxidation products
Abstract
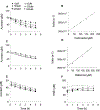
Endogenous histidyl dipeptides such as carnosine (β-alanine-L-histidine) form conjugates with lipid peroxidation products such as 4-hydroxy-trans-2-nonenal (HNE and acrolein), chelate metals, and protect against myocardial ischemic injury. Nevertheless, it is unclear whether these peptides protect against cardiac injury by directly reacting with lipid peroxidation products. Hence, to examine whether changes in the structure of carnosine could affect its aldehyde reactivity and metal chelating ability, we synthesized methylated analogs of carnosine, balenine (β-alanine-Nτ-methylhistidine) and dimethyl balenine (DMB), and measured their aldehyde reactivity and metal chelating properties. We found that methylation of Nτ residue of imidazole ring (balenine) or trimethylation of carnosine backbone at Nτ residue of imidazole ring and terminal amine group dimethyl balenine (DMB) abolishes the ability of these peptides to react with HNE. Incubation of balenine with acrolein resulted in the formation of single product (m/z 297), whereas DMB did not react with acrolein. In comparison with carnosine, balenine exhibited moderate acrolein quenching capacity. The Fe2+ chelating ability of balenine was higher than that of carnosine, whereas DMB lacked chelating capacity. Pretreatment of cardiac myocytes with carnosine increased the mean lifetime of myocytes superfused with HNE or acrolein compared with balenine or DMB. Collectively, these results suggest that carnosine protects cardiac myocytes against HNE and acrolein toxicity by directly reacting with these aldehydes. This reaction involves both the amino group of β-alanyl residue and the imidazole residue of L-histidine. Methylation of these sites prevents or abolishes the aldehyde reactivity of carnosine, alters its metal-chelating property, and diminishes its ability to prevent electrophilic injury.
Keywords: 4-Hydroxy-trans-2-nonenal; Acrolein; Cardiac myocytes; Histidyl dipeptides.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest
All authors declare that no competing financial interest exists.
Figures


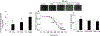

Similar articles
-
Cardiospecific Overexpression of ATPGD1 (Carnosine Synthase) Increases Histidine Dipeptide Levels and Prevents Myocardial Ischemia Reperfusion Injury.J Am Heart Assoc. 2020 Jun 16;9(12):e015222. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.119.015222. Epub 2020 Jun 9. J Am Heart Assoc. 2020. PMID: 32515247 Free PMC article.
-
Carnosine and related dipeptides as quenchers of reactive carbonyl species: from structural studies to therapeutic perspectives.Biofactors. 2005;24(1-4):77-87. doi: 10.1002/biof.5520240109. Biofactors. 2005. PMID: 16403966
-
Acrolein-sequestering ability of endogenous dipeptides: characterization of carnosine and homocarnosine/acrolein adducts by electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry.J Mass Spectrom. 2003 Sep;38(9):996-1006. doi: 10.1002/jms.517. J Mass Spectrom. 2003. PMID: 14505328
-
Aldehyde-sequestering drugs: tools for studying protein damage by lipid peroxidation products.Toxicology. 2002 Dec 27;181-182:229-36. doi: 10.1016/s0300-483x(02)00287-1. Toxicology. 2002. PMID: 12505316 Review.
-
Biosynthesis of Carnosine and Related Dipeptides in Vertebrates.Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2018;19(8):771-789. doi: 10.2174/1389203719666180226155657. Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2018. PMID: 29484990 Review.
Cited by
-
Acrolein-inducing ferroptosis contributes to impaired peripheral neurogenesis in zebrafish.Front Neurosci. 2023 Jan 12;16:1044213. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2022.1044213. eCollection 2022. Front Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 36711148 Free PMC article.
-
Small extracellular vesicles from young adipose-derived stem cells ameliorate age-related changes in the heart of old mice.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2025 Mar 13;16(1):138. doi: 10.1186/s13287-025-04255-z. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2025. PMID: 40082997 Free PMC article.
-
Inhalation of concentrated ambient PM2.5 promotes inactivation of telomerase reverse transcriptase, telomere shortening, and senescence of multiple cell types in mice.Toxicol Sci. 2025 Jul 1;206(1):147-157. doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kfaf045. Toxicol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40172909
-
Reactive Oxygen Species-Induced Lipid Peroxidation in Apoptosis, Autophagy, and Ferroptosis.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2019 Oct 13;2019:5080843. doi: 10.1155/2019/5080843. eCollection 2019. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2019. PMID: 31737171 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Trehalose-Carnosine Prevents the Effects of Spinal Cord Injury Through Regulating Acute Inflammation and Zinc(II) Ion Homeostasis.Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2023 May;43(4):1637-1659. doi: 10.1007/s10571-022-01273-w. Epub 2022 Sep 19. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2023. PMID: 36121569 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abe H (2000) Role of histidine-related compounds as intracellular proton buffering constituents in vertebrate muscle. Biochemistry (Mosc) 65 (7):757–765 - PubMed
-
- Aldini G, Carini M, Beretta G, Bradamante S, Facino RM (2002) Carnosine is a quencher of 4hydroxy-nonenal: through what mechanism of reaction? Biochem Biophys Res Commun 298 (5):699–706 - PubMed
-
- Baba SP, Zhang D, Singh M, Dassanayaka S, Xie Z, Jagatheesan G, Zhao J, Schmidtke VK, Brittian KR, Merchant ML, Conklin DJ, Jones SP, Bhatnagar A (2018) Deficiency of aldose reductase exacerbates early pressure overload-induced cardiac dysfunction and autophagy in mice. J Mol Cell Cardiol 118:183–192. doi:10.1016/j.yjmcc.2018.04.002 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Baran EJ (2000) Metal complexes of carnosine. Biochemistry (Mosc) 65 (7):789–797 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

