Transcription Factors Activate Genes through the Phase-Separation Capacity of Their Activation Domains
- PMID: 30449618
- PMCID: PMC6295254
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2018.10.042
Transcription Factors Activate Genes through the Phase-Separation Capacity of Their Activation Domains
Abstract
Gene expression is controlled by transcription factors (TFs) that consist of DNA-binding domains (DBDs) and activation domains (ADs). The DBDs have been well characterized, but little is known about the mechanisms by which ADs effect gene activation. Here, we report that diverse ADs form phase-separated condensates with the Mediator coactivator. For the OCT4 and GCN4 TFs, we show that the ability to form phase-separated droplets with Mediator in vitro and the ability to activate genes in vivo are dependent on the same amino acid residues. For the estrogen receptor (ER), a ligand-dependent activator, we show that estrogen enhances phase separation with Mediator, again linking phase separation with gene activation. These results suggest that diverse TFs can interact with Mediator through the phase-separating capacity of their ADs and that formation of condensates with Mediator is involved in gene activation.
Keywords: activation domain; gene activation; mediator; phase separation; transcription; transcription factor.
Copyright © 2018 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
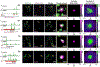
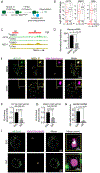
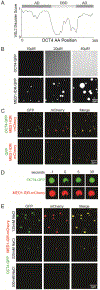
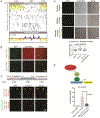
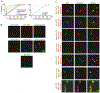
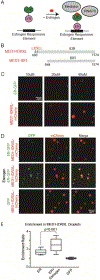
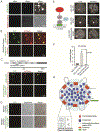
Comment in
-
Phase Separation, Protein Disorder, and Enhancer Function.Cell. 2018 Dec 13;175(7):1723-1725. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2018.11.034. Cell. 2018. PMID: 30550782
References
-
- Alberti S (2017). The wisdom of crowds: regulating cell function through condensed states of living matter. J. Cell Sci. 130, 2789–2796. - PubMed
-
- Arany Z, Newsome D, Oldread E, Livingston DM, and Eckner R (1995). A family of transcriptional adaptor proteins targeted by the E1A oncoprotein. Nature 374, 81–84. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

