Ceritinib Aggravates Glycemic Control in Insulin-treated Patients with Diabetes and Metastatic ALK-positive Lung Cancer
- PMID: 30449809
- PMCID: PMC6465015
- DOI: 10.2169/internalmedicine.1870-18
Ceritinib Aggravates Glycemic Control in Insulin-treated Patients with Diabetes and Metastatic ALK-positive Lung Cancer
Abstract
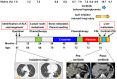
We herein report a 75-year-old woman with insulin-treated diabetes and metastatic anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK)-rearranged non-small cell lung cancer who received ceritinib, a second-generation ALK inhibitor, and achieved dramatic tumor reduction. However, her fasting blood glucose increased, particularly markedly in the first two weeks after ceritinib administration, and did not normalize even increasing the total insulin dose. After discontinuing ceritinib, her glucose levels rapidly reduced. Ceritinib can aggravate hyperglycemia in patients with diabetes who lack compensatory insulin secretion, due to its inhibitory effects on the insulin receptor. Careful monitoring for ceritinib-induced hyperglycemia should be performed, especially in the first two weeks after ceritinib administration.
Keywords: ceritinib; hyperglycemia; insulin resistance.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



References
-
- Soda M, Choi YL, Enomoto M, et al. Identification of the transforming EML4-ALK fusion gene in non-small-cell lung cancer. Nature 448: 561-566, 2007. - PubMed
-
- Mok TSK, Crino L, Felip E, et al. The accelerated path of ceritinib: translating pre-clinical development into clinical efficacy. Cancer Treat Rev 55: 181-189, 2017. - PubMed
-
- Khozin S, Blumenthal GM, Zhang L, et al. FDA approval: ceritinib for the treatment of metastatic anaplastic lymphoma kinase-positive non-small cell lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res 21: 2436-2439, 2015. - PubMed

