Robust Co-clustering to Discover Toxicogenomic Biomarkers and Their Regulatory Doses of Chemical Compounds Using Logistic Probabilistic Hidden Variable Model
- PMID: 30450112
- PMCID: PMC6225736
- DOI: 10.3389/fgene.2018.00516
Robust Co-clustering to Discover Toxicogenomic Biomarkers and Their Regulatory Doses of Chemical Compounds Using Logistic Probabilistic Hidden Variable Model
Abstract
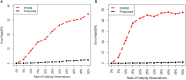
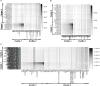
Detection of biomarker genes and their regulatory doses of chemical compounds (DCCs) is one of the most important tasks in toxicogenomic studies as well as in drug design and development. There is an online computational platform "Toxygates" to identify biomarker genes and their regulatory DCCs by co-clustering approach. Nevertheless, the algorithm of that platform based on hierarchical clustering (HC) does not share gene-DCC two-way information simultaneously during co-clustering between genes and DCCs. Also it is sensitive to outlying observations. Thus, this platform may produce misleading results in some cases. The probabilistic hidden variable model (PHVM) is a more effective co-clustering approach that share two-way information simultaneously, but it is also sensitive to outlying observations. Therefore, in this paper we have proposed logistic probabilistic hidden variable model (LPHVM) for robust co-clustering between genes and DCCs, since gene expression data are often contaminated by outlying observations. We have investigated the performance of the proposed LPHVM co-clustering approach in a comparison with the conventional PHVM and Toxygates co-clustering approaches using simulated and real life TGP gene expression datasets, respectively. Simulation results show that the proposed method improved the performance over the conventional PHVM in presence of outliers; otherwise, it keeps equal performance. In the case of real life TGP data analysis, three DCCs (glibenclamide-low, perhexilline-low, and hexachlorobenzene-medium) for glutathione metabolism pathway dataset as well as two DCCs (acetaminophen-medium and methapyrilene-low) for PPAR signaling pathway dataset were incorrectly co-clustered by the Toxygates online platform, while only one DCC (hexachlorobenzene-low) for glutathione metabolism pathway was incorrectly co-clustered by the proposed LPHVM approach. Our findings from the real data analysis are also supported by the other findings in the literature.
Keywords: co-clustering; doses of chemical compounds (DCCs); logistic probabilistic hidden variable model (LPHVM); logistic transformation; outlying observations; probabilistic hidden variable model (PHVM); toxicogenomic biomarker.
Figures
References
-
- Agostinelli C. C., Leung A., Yohai V. J., Zamar R. H. (2015). Robust estimation of multivariate location and scatter in the presence of cellwise and casewise contamination. Test 24, 441–461. 10.1007/s11749-015-0450-6 - DOI
-
- Alqallaf F., Van A. S., Yohai V., Zamar R. (2009). Propagation of outliers in multivariate data. Ann. Stat. 37, 311–331. 10.1214/07-AOS588 - DOI
-
- Atkinson A. C. (1982). Regression diagnostics, transformation and constructed variables. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B 44, 1–36.
-
- Bicego M., Lovato P., Ferrarini A., Delledonne M. (2010). Biclustering of expression microarray data with topic models in International Conference on Pattern Recognition (Washington, DC: IEEE Computer Society; ), 2728–2731. 10.1109/ICPR.2010.668 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

