Nonadiabatic dynamics: The SHARC approach
- PMID: 30450129
- PMCID: PMC6220962
- DOI: 10.1002/wcms.1370
Nonadiabatic dynamics: The SHARC approach
Abstract
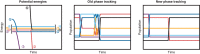
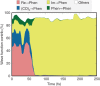
We review the Surface Hopping including ARbitrary Couplings (SHARC) approach for excited-state nonadiabatic dynamics simulations. As a generalization of the popular surface hopping method, SHARC allows simulating the full-dimensional dynamics of molecules including any type of coupling terms beyond nonadiabatic couplings. Examples of these arbitrary couplings include spin-orbit couplings or dipole moment-laser field couplings, such that SHARC can describe ultrafast internal conversion, intersystem crossing, and radiative processes. The key step of the SHARC approach consists of a diagonalization of the Hamiltonian including these couplings, such that the nuclear dynamics is carried out on potential energy surfaces including the effects of the couplings-this is critical in any applications considering, for example, transition metal complexes or strong laser fields. We also give an overview over the new SHARC2.0 dynamics software package, released under the GNU General Public License, which implements the SHARC approach and several analysis tools. The review closes with a brief survey of applications where SHARC was employed to study the nonadiabatic dynamics of a wide range of molecular systems. This article is categorized under: Theoretical and Physical Chemistry > Reaction Dynamics and KineticsSoftware > Simulation MethodsSoftware > Quantum Chemistry.
Keywords: Ab initio molecular dynamics; SHARC; excited states; nonadiabatic dynamics; surface hopping.
Figures



References
FURTHER READING
-
- The SHARC2.0 package and the WFOVERLAP program, as well as comprehensive documentation and tutorials, can be obtained at http://sharc-md.org/
References
-
- Amatatsu, Y. , Morokuma, K. , & Yabushita, S. (1991). Ab initio potential energy surfaces and trajectory studies of A‐band photodissociation dynamics: CH3I*→ CH3 + I and CH3 + I* . The Journal of Chemical Physics, 94(7), 4858–4876. 10.1063/1.460571 - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
