Down-regulation of AR splice variants through XPO1 suppression contributes to the inhibition of prostate cancer progression
- PMID: 30450161
- PMCID: PMC6219671
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.26239
Down-regulation of AR splice variants through XPO1 suppression contributes to the inhibition of prostate cancer progression
Abstract
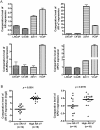
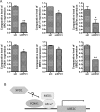
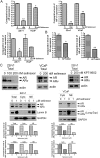
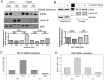
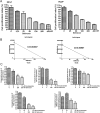
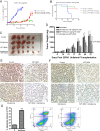
Emerging studies have shown that the expression of AR splice variants (ARv) lacking ligand-binding domain is associated with castrate-resistant prostate cancer (CRPC) and higher risk of tumor metastasis and recurrence. Nuclear export protein XPO1 regulates the nuclear localization of many proteins including tumor suppressor proteins. Increased XPO1 in prostate cancer is associated with a high Gleason score and bone metastasis. In this study, we found that high expression of AR splice variant 7 (AR-v7) was correlated with increased XPO1 expression. Silencing of XPO1 by RNAi or treatment with Selective Inhibitor of Nuclear Export (SINE) compounds selinexor and eltanexor (KPT-8602) down-regulated the expression of AR, AR-v7 and ARv567es at mRNA and protein levels. XPO1 silencing also inhibited the expression of AR and ARv regulators including FOXA1, Src, Vav3, MED1 and Sam68, leading to the suppression of ARv and AR target genes, UBE2C and PSA. By targeting XPO1/ARv signaling, SINE suppressed prostate cancer (PCa) growth in vitro and in vivo and potentiated the anti-cancer activity of anti-AR agents, enzalutamide and abiraterone. Therefore, XPO1 inhibition could be a novel promising agent used in combination with conventional chemotherapeutics and AR-targeted therapy for the better treatment of PCa, especially CRPC.
Keywords: AR SPLICE variant; CRM1; SINE; metastatic prostate cancer; nuclear export.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST William Senapedis, Erkan Baloglu, Yosef Landesman, Michael Kauffman, Christian Argueta, Trinayan Kashyap, Hua Chang and Sharon Shacham are employees of Karyopharm Therapeutics and hold patents, equity and stocks and have received both major and minor remunerations from Karyopharm. All other authors have no potential conflict of interests.
Figures

Comment in
-
Selective inhibitors of nuclear export: potential therapeutics for AR variant-expressing prostate cancer.Oncotarget. 2018 Nov 9;9(88):35797-35798. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.26296. eCollection 2018 Nov 9. Oncotarget. 2018. PMID: 30533190 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer Statistics, 2017. CA Cancer J Clin. 2017;67:7–30. - PubMed
-
- Donovan MJ, Osman I, Khan FM, Vengrenyuk Y, Capodieci P, Koscuiszka M, Anand A, Cordon-Cardo C, Costa J, Scher HI. Androgen receptor expression is associated with prostate cancer-specific survival in castrate patients with metastatic disease. BJU Int. 2010;105:462–67. - PubMed
-
- Sircar K, Yoshimoto M, Monzon FA, Koumakpayi IH, Katz RL, Khanna A, Alvarez K, Chen G, Darnel AD, Aprikian AG, Saad F, Bismar TA, Squire JA. PTEN genomic deletion is associated with p-Akt and AR signalling in poorer outcome, hormone refractory prostate cancer. J Pathol. 2009;218:505–13. - PubMed
-
- de la Taille A, Rubin MA, Chen MW, Vacherot F, de Medina SG, Burchardt M, Buttyan R, Chopin D. Beta-catenin-related anomalies in apoptosis-resistant and hormone-refractory prostate cancer cells. Clin Cancer Res. 2003;9:1801–07. - PubMed
-
- Azoulay S, Terry S, Chimingqi M, Sirab N, Faucon H, Gil Diez de Medina S, Moutereau S, Maillé P, Soyeux P, Abbou C, Salomon L, Vacherot F, de La Taille A, et al. Comparative expression of Hedgehog ligands at different stages of prostate carcinoma progression. J Pathol. 2008;216:460–70. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

