Preventive Effect of Hydroalcoholic Extract of Rosa damascena on Cardiovascular Parameters in Acute Hypertensive Rats Induced by Angiotensin II
- PMID: 30450175
- PMCID: PMC6202776
- DOI: 10.4103/ijpvm.IJPVM_312_17
Preventive Effect of Hydroalcoholic Extract of Rosa damascena on Cardiovascular Parameters in Acute Hypertensive Rats Induced by Angiotensin II
Abstract
Background: Rosa damascena (R.D) is an aromatic plant with numerous therapeutic effects including cardiovascular effect. The mechanism cardiovascular effect of R.D is unclear and suggested mediated through renin-angiotensin system (RAS). Therefore, in this study, the role of hydroalcoholic extract of R.D on acute hypertension induced by AngII was evaluated.
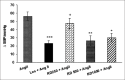
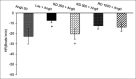
Methods: After anesthesia, femoral artery and vein of rats were cannulated for recording cardiovascular responses and drug injection, respectively. Systolic blood pressure (SBP), mean arterial blood pressure (MAP), and heart rate (HR) were recorded continuously by power lab software. Rats were divided into saline, AngII (50 ng/kg), AngII + Losartan (10 mg/kg), and three groups of R.D extract (250, 500, and 1000 mg/kg). Losartan and AngII were administered intravenously and the other ones intraperitoneal. In the R.D groups, 30 min after injection of the extract, AngII was injected and the maximum changes in SBP, MAP, and HR were calculated and compared to that in control and AngII groups.
Results: Results show that AngII significantly increased SBP, MAP, and decreased HR than the control group which was blocked by losartan. SBP and MAP in R.D + AngII groups were significantly lower than AngII alone (P < 0.05 -P < 0.001). Only MAP in higher dose (1000 mg/kg) was significantly lower than low dose (250 mg/kg; P < 0.05). Two higher doses also significantly decreased bradycardia induced by AngII (P < 0. 01).
Conclusions: The preventive effect of hydroalcoholic extract of R.D on cardiovascular parameters maybe is mediated by suppression of AngII activity.
Keywords: Angiotensin II; Rosa damascena; blood pressure; heart rate; rennin–angiotensin system.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest
Figures


References
-
- Hongratanaworakit T. Relaxing effect of rose oil on humans. Nat Prod Commun. 2009;4:291–6. - PubMed
-
- Hummer KE, Janick J. Genetics and Genomics of Rosaceae. New York: Springer; 2009. Rosaceae: taxonomy, economic importance, genomics; pp. 1–17.
-
- Yassa N, Masoomi F, Rankouhi SR, Hadjiakhoondi A. Chemical composition and antioxidant activity of the extract and essential oil of Rosa damascena from Iran, population of Guilan. DARU. 2015;17:175–80.
-
- Babu KG, Singh B, Joshi VP, Singh V. Essential oil composition of Damask rose (Rosa damascena Mill.) distilled under different pressures and temperatures. Flavour Fragrance J. 2002;17:136–40.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

