Equine lung decellularization: a potential approach for in vitro modeling the role of the extracellular matrix in asthma
- PMID: 30450188
- PMCID: PMC6236489
- DOI: 10.1177/2041731418810164
Equine lung decellularization: a potential approach for in vitro modeling the role of the extracellular matrix in asthma
Abstract
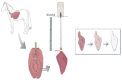
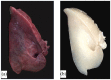
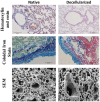
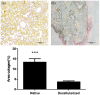
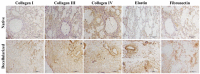
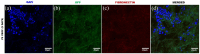
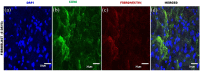
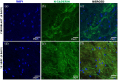
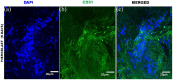
Contrary to conventional research animals, horses naturally develop asthma, a disease in which the extracellular matrix of the lung plays a significant role. Hence, the horse lung extracellular matrix appears to be an ideal candidate model for in vitro studying the mechanisms and potential treatments for asthma. However, so far, such model to study cell-extracellular matrix interactions in asthma has not been developed. The aim of this study was to establish a protocol for equine lung decellularization that maintains the architecture of the extracellular matrix and could be used in the future as an in vitro model for therapeutic treatment in asthma. For this the equine lungs were decellularized by sodium dodecyl sulfate detergent perfusion at constant gravitational pressure of 30 cmH2O. Lung scaffolds were assessed by immunohistochemistry (collagen I, III, IV, laminin, and fibronectin), scanning electron microscopy, and DNA quantification. Their mechanical property was assessed by measuring lung compliance using the super-syringe technique. The optimized protocol of lung equine decellularization was effective to remove cells (19.8 ng/mg) and to preserve collagen I, III, IV, laminin, and fibronectin. Moreover, scanning electron microscopy analysis demonstrated maintained microscopic lung structures. The decellularized lungs presented lower compliance compared to native lung. In conclusion we described a reproducible decellularization protocol that can produce an acellular equine lung feasible for the future development of novel treatment strategies in asthma.
Keywords: Equine lung; asthma; decellularized; extracellular matrix; respiratory diseases.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of conflicting interests: The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures

References
-
- World Health Organization. Media centre fact sheets as of April 2017, http://www.who.int (accessed 3 September 2017).
-
- Clienti S, Morjaria JB, Basile E, et al. Monoclonal antibodies for the treatment of severe asthma. Curr Allergy Asthma Rep 2011; 11: 253–260. - PubMed
-
- Giembycz MA, Newton R. Harnessing the clinical efficacy of phosphodiesterase 4 inhibitors in inflammatory lung diseases: dual-selective phosphodiesterase inhibitors and novel combination therapies. Handb Exp Pharmacol 2011; 204: 415–446. - PubMed
-
- Nair P, Gaga M, Zervas E, et al. Safety and efficacy of a CXCR2 antagonist in patients with severe asthma and sputum neutrophils: a randomized, placebo-controlled clinical trial. Clin Exp Allergy 2012; 42: 1097–1103. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

