Augmented Cardiopulmonary Baroreflex Sensitivity in Intradialytic Hypertension
- PMID: 30450466
- PMCID: PMC6224617
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ekir.2018.07.025
Augmented Cardiopulmonary Baroreflex Sensitivity in Intradialytic Hypertension
Abstract
Introduction: End-stage renal disease (ESRD) patients with a paradoxical increase in blood pressure (BP) during hemodialysis (HD), termed intradialytic hypertension (ID-HTN), are at significantly increased risk for mortality and adverse cardiovascular events. ID-HTN affects up to 15% of all HD patients, and the pathophysiologic mechanisms remain unknown. We hypothesized that ESRD patients prone to ID-HTN have heightened volume-sensitive cardiopulmonary baroreflex sensitivity (BRS) that leads to exaggerated increases in sympathetic nervous system (SNS) activation during HD.
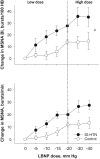
Methods: We studied ESRD patients on maintenance HD with ID-HTN (n = 10) and without ID-HTN (controls, n = 12) on an interdialytic day, 24 to 30 hours after their last HD session. We measured continuous muscle sympathetic nerve activity (MSNA), beat-to-beat arterial BP, and electrocardiography (ECG) at baseline, and during graded lower body negative pressure (LBNP). Low-dose LBNP isolates cardiopulmonary BRS, whereas higher doses allow assessment of physiologic responses to orthostatic stress.
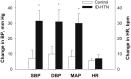
Results: The ID-HTN patients had significantly higher pre- and post-HD BP, and greater interdialytic fluid weight gain compared to controls. There was a significantly greater increase in MSNA burst incidence (P = 0.044) during graded LBNP in the ID-HTN group, suggesting heightened cardiopulmonary BRS. The ID-HTN group also had a trend toward increased diastolic BP response during LBNP, and had significantly greater increases in BP during the cold pressor test.
Conclusion: Patients with ID-HTN have augmented cardiopulmonary BRS that may contribute to increased SNS activation and BP response during HD.
Keywords: baroreflex; end-stage renal disease; hemodialysis; sympathetic activity.
Figures