Mature outcomes and prognostic indices in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma in Malawi: a prospective cohort
- PMID: 30450671
- PMCID: PMC6340743
- DOI: 10.1111/bjh.15625
Mature outcomes and prognostic indices in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma in Malawi: a prospective cohort
Abstract
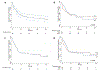
Outcomes for diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) in sub-Saharan Africa (SSA) are poorly described. We report mature data from one of the first prospective SSA cohorts. Patients aged ≥18 years with DLBCL were enrolled in Malawi 2013-2017. Participants were treated with CHOP (cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, prednisone) chemotherapy and concurrent antiretroviral therapy (ART) if positive for human immunodeficiency virus (HIV+). Eighty-six participants (mean age 47 years, standard deviation 13) were enrolled: 54 (63%) were male and 51 (59%) were HIV+, of whom 34 (67%) were on ART at DLBCL diagnosis. Median CD4 count was 0·113 cells × 109 /l (interquartile range [IQR] 0·062-0·227) and 25 (49%) had HIV viral load <400 copies/μl. Participants received median six cycles CHOP (IQR 4-6). No patients were lost to follow-up and the 2-year overall survival was 38% (95% confidence interval 28-49). In multivariable analyses, Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group performance status (PS) ≥2 and lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) >2× upper limit of normal (ULN) were associated with mortality. HIV status was not associated with mortality. A simplified prognostic model of LDH >2× ULN and PS ≥2 performed at least as well as the age-adjusted International Prognostic Index. DLBCL can be successfully treated in SSA and outcomes did not differ by HIV status. A simplified prognostic model prognosticates well and may be easier to use in resource-limited settings but requires validation.
Keywords: chemotherapy; diffuse large B-cell lymphoma; human immunodeficiency virus; prognosis; sub-Saharan Africa.
© 2018 British Society for Haematology and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
AUTHORS DISCLOSURES OF POTENTIAL CONFLICTS OF INTEREST
None of the authors have any have conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures
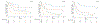
References
-
- Baptista MJ, Garcia O, Morgades M, Gonzalez-Barca E, Miralles P, Lopez-Guillermo A, Abella E, Moreno M, Sancho JM, Feliu E, Ribera JM & Navarro JT (2015) HIV-infection impact on clinical-biological features and outcome of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma treated with R-CHOP in the combination antiretroviral therapy era. AIDS, 29, 811–818. - PubMed
-
- Bateganya MH, Stanaway J, Brentlinger PE, Magaret AS, Wald A, Orem J & Casper C (2011) Predictors of survival after a diagnosis of non-Hodgkin lymphoma in a resource-limited setting: a retrospective study on the impact of HIV infection and its treatment. Journal of Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndromes, 56, 312–319. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Besson C, Lancar R, Prevot S, Algarte-Genin M, Delobel P, Bonnet F, Meyohas MC, Partisani M, Oberic L, Gabarre J, Goujard C, Boue F, Coppo P, Costello R, Hendel-Chavez H, Mekerri N, Dos Santos G, Recher C, Delarue R, Casasnovas RO, Taoufik Y, Mounier N, Costagliola D & Cohort A-CL (2017) Outcomes for HIV-associated diffuse large B-cell lymphoma in the modern combined antiretroviral therapy era. AIDS, 31, 2493–2501. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

