The Brain Donation Program in South Korea
- PMID: 30450854
- PMCID: PMC6240560
- DOI: 10.3349/ymj.2018.59.10.1197
The Brain Donation Program in South Korea
Abstract
Purpose: Obtaining brain tissue is critical to definite diagnosis and to furthering understanding of neurodegenerative diseases. The present authors have maintained the National Neuropathology Reference and Diagnostic Laboratories for Dementia in South Korea since 2016. We have built a nationwide brain bank network and are collecting brain tissues from patients with neurodegenerative diseases. We are aiming to facilitate analyses of clinic-pathological and image-pathological correlations of neurodegenerative disease and to broaden understanding thereof.
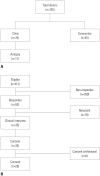
Materials and methods: We recruited participants through two routes: from memory clinics and the community. As a baseline evaluation, clinical interviews, a neurological examination, laboratory tests, neuropsychological tests, and MRI were undertaken. Some patients also underwent amyloid PET.
Results: We recruited 105 participants, 70 from clinics and 35 from the community. Among them, 11 died and were autopsied. The clinical diagnoses of the autopsied patients included four with Alzheimer's disease (AD), two with subcortical vascular dementia, two with non-fluent variant primary progressive aphasia, one with leukoencephalopathy, one with frontotemporal dementia (FTD), and one with Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (CJD). Five patients underwent amyloid PET: two with AD, one with mixed dementia, one with FTD, and one with CJD.
Conclusion: The clinical and neuropathological information to be obtained from this cohort in the future will provide a deeper understanding of the neuropathological mechanisms of cognitive impairment in Asia, especially Korea.
Keywords: Alzheimer's disease; Neuropathology; amyloid; brain autopsy; frontotemporal dementia.
© Copyright: Yonsei University College of Medicine 2018.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no financial conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Lim A, Tsuang D, Kukull W, Nochlin D, Leverenz J, McCormick W, et al. Clinico-neuropathological correlation of Alzheimer's disease in a community-based case series. J Am Geriatr Soc. 1999;47:564–569. - PubMed
-
- Kang Y, Na DL. Seoul Neuropsychological Screening Battery (SNSB) Incheon: Human Brain Research & Consulting; 2003.
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

