miR-34a Inhibitor May Effectively Protect against Sevoflurane-Induced Hippocampal Apoptosis through the Wnt/β-Catenin Pathway by Targeting Wnt1
- PMID: 30450855
- PMCID: PMC6240572
- DOI: 10.3349/ymj.2018.59.10.1205
miR-34a Inhibitor May Effectively Protect against Sevoflurane-Induced Hippocampal Apoptosis through the Wnt/β-Catenin Pathway by Targeting Wnt1
Abstract
Purpose: Research has shown that sevoflurane-induced toxicity causes neurodegeneration in the developing brain. miR-34a has been found to negatively regulate ketamine-induced hippocampal apoptosis and memory impairment. However, the role of miR-34a in sevoflurane-induced hippocampal neurodegeneration remains largely unclear.
Materials and methods: C57/BL6 mice (7-day-old) inhaled 2.3% sevoflurane for 2 h/day over 3 consecutive days. miR-34a expression was reduced through intracerebroventricular injection with miR-34a interference lentivirus vector (LV-anti-miR-34a) into mouse hippocampus after anesthesia on the first day of exposure. Hippocampal apoptosis was detected by TUNEL assay and flow cytometry analysis. Spatial memory ability was evaluated by the Morris water maze test. The interaction between miR-34a and Wnt1 was confirmed by luciferase reporter assay, RNA immunoprecipitation, Western blot, and immunofluorescence staining. The effects of miR-34a on protein levels of B-cell lymphoma 2 (Bcl-2), bcl-2-like protein 4 (Bax), and Wnt/β-catenin pathway-related proteins were evaluated using Western blot analysis.
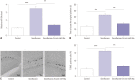
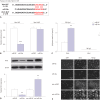
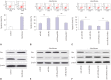
Results: Sevoflurane upregulated hippocampal miR-34a, and miR-34a inhibitor attenuated sevoflurane-induced hippocampal apoptosis and memory impairment. miR-34a negatively regulated Wnt1 expression by targeting miR-34a in hippocampal neurons. Moreover, forced expression of Wnt1 markedly undermined miR-34a-mediated enhancement of sevoflurane-induced apoptosis of hippocampal neurons, while Wnt1 silencing greatly restored anti-miR-34a-mediated repression of sevoflurane-induced apoptosis of hippocampal neurons. Increased expression of miR-34a inhibited the Wnt/β-catenin pathway in hippocampal neurons exposed to sevoflurane, while anti-miR-34a exerted the opposite effects.
Conclusion: miR-34a inhibitor may effectively protect against sevoflurane-induced hippocampal apoptosis via activation of the Wnt/β-catenin pathway by targeting Wnt1.
Keywords: Wnt/β-catenin pathway; Wnt1; hippocampal apoptosis; miR-34a; sevoflurane.
© Copyright: Yonsei University College of Medicine 2018.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no financial conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Hu N, Guo D, Wang H, Xie K, Wang C, Li Y, et al. Involvement of the blood-brain barrier opening in cognitive decline in aged rats following orthopedic surgery and high concentration of sevoflurane inhalation. Brain Res. 2014;1551:13–24. - PubMed
-
- Zhang X, Xue Z, Sun A. Subclinical concentration of sevoflurane potentiates neuronal apoptosis in the developing C57BL/6 mouse brain. Neurosci Lett. 2008;447:109–114. - PubMed
-
- Pan Z, Lu XF, Shao C, Zhang C, Yang J, Ma T, et al. The effects of sevoflurane anesthesia on rat hippocampus: a genomic expression analysis. Brain Res. 2011;1381:124–133. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

