Active coping moderates associations among race-related stress, rumination, and depressive symptoms in emerging adult African American women
- PMID: 30451137
- PMCID: PMC6839900
- DOI: 10.1017/S0954579418001268
Active coping moderates associations among race-related stress, rumination, and depressive symptoms in emerging adult African American women
Abstract
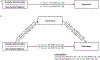
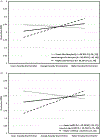
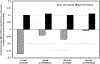
Cross-sectional and longitudinal research has shown that race-related stress is associated with increased depressive symptoms among racial/ethnic minorities. Rumination has long been considered a maladaptive self-regulatory response to race-related stress, and growing evidence suggests that it may be an important link in the relation between race-related stress and depression. More adaptive forms of self-regulation, such as active coping, may counteract the negative impact of rumination. We examined the influence of rumination on the relation between race-related stress and depressive symptoms in a sample (N = 69) of young adult (mean age = 20 ± 1.5 years) African American women. We also considered the possible moderating effects of John Henryism, a form of persistent and determined goal striving, and vagally mediated heart rate variability, a purported biomarker of coping. Anticipatory race-related stress was indirectly associated with depressive symptoms through rumination: estimate = 0.07, 95% confidence interval [0.01, 0.16]. Both John Henryism and vagally mediated heart rate variability moderated the relationship between race-related stress and rumination; however, only John Henryism reliably influenced the indirect association between race-related stress and depression through rumination. We discuss these findings in the context of growing research examining the interplay between cultural and biological factors in the risk for poorer mental health.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Developmental differences in the impact of racial discrimination on depression and anxiety among Black youth: Examining rumination as a mechanism.Am J Orthopsychiatry. 2023;93(4):293-303. doi: 10.1037/ort0000679. Epub 2023 May 8. Am J Orthopsychiatry. 2023. PMID: 37155290 Free PMC article.
-
Autonomic regulation in response to stress: The influence of anticipatory emotion regulation strategies and trait rumination.Emotion. 2019 Apr;19(3):443-454. doi: 10.1037/emo0000448. Epub 2018 May 21. Emotion. 2019. PMID: 29781647
-
Drinking to Cope With Depressive Symptoms and Ruminative Thinking: A Multiple Mediation Model Among College Students.Subst Use Misuse. 2017 Jan 2;52(1):52-62. doi: 10.1080/10826084.2016.1214151. Epub 2016 Sep 26. Subst Use Misuse. 2017. PMID: 27668861 Free PMC article.
-
High-Effort Coping and Cardiovascular Disease among Women: A Systematic Review of the John Henryism Hypothesis.J Urban Health. 2019 Mar;96(Suppl 1):12-22. doi: 10.1007/s11524-018-00333-1. J Urban Health. 2019. PMID: 30506136 Free PMC article.
-
The Relationship Between Co-rumination and Depressive Symptoms: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.J Youth Adolesc. 2025 Jun;54(6):1551-1569. doi: 10.1007/s10964-025-02140-9. Epub 2025 Feb 1. J Youth Adolesc. 2025. PMID: 39891852
Cited by
-
Racial Stress and Trauma and the Development of Adolescent Depression: A Review of the Role of Vigilance Evoked by Racism-Related Threat.Chronic Stress (Thousand Oaks). 2022 Aug 9;6:24705470221118574. doi: 10.1177/24705470221118574. eCollection 2022 Jan-Dec. Chronic Stress (Thousand Oaks). 2022. PMID: 35966451 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Systematic Review of Black People Coping With Racism: Approaches, Analysis, and Empowerment.Perspect Psychol Sci. 2023 Mar;18(2):392-415. doi: 10.1177/17456916221100509. Epub 2022 Aug 25. Perspect Psychol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36006823 Free PMC article.
-
An evolutionary concept analysis of depression in Black mothers.Arch Psychiatr Nurs. 2024 Dec;53:9-16. doi: 10.1016/j.apnu.2024.08.001. Epub 2024 Aug 17. Arch Psychiatr Nurs. 2024. PMID: 39615951 Review.
-
The wear and tear of racism: Self-silencing from the perspective of young Black women.SSM Qual Res Health. 2023 Jun;3:100268. doi: 10.1016/j.ssmqr.2023.100268. Epub 2023 Apr 10. SSM Qual Res Health. 2023. PMID: 37576489 Free PMC article.
-
Rumination as a Mediator of the Association Between Racial Discrimination and Depression Among Black Youth.J Racial Ethn Health Disparities. 2022 Oct;9(5):1937-1945. doi: 10.1007/s40615-021-01132-2. Epub 2021 Aug 19. J Racial Ethn Health Disparities. 2022. PMID: 34410607 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Anderson NB, McNeilly M, & Myers H. (1992). Toward understanding race difference in autonomic reactivity In Turner JR, Sherwood A, & Light KC (Eds.), Individual differences in cardiovascular response to stress (pp. 125–145). New York: Springer.
-
- Appelhans BM, & Luecken LJ (2006). Heart rate variability as an index of regulated emotional responding. Review of General Psychology, 10, 229–240. doi:10.1037/1089-2680.10.3.229 - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

